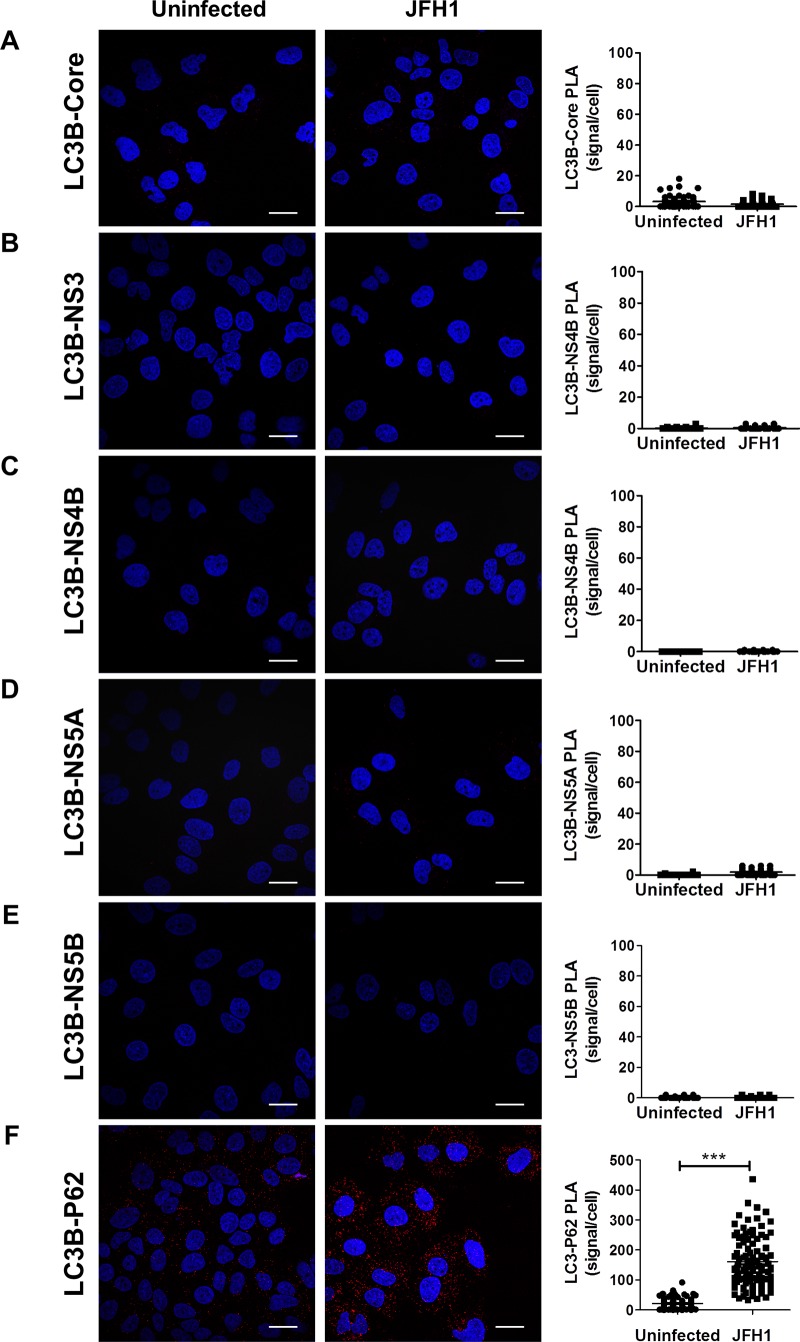
Fig 9. Assessment of LC3 interactions with viral proteins in infected cells as observed by proximity-ligation assay (PLA).
JFH1-infected at more than 90% or uninfected cells were fixed and processed for detection of LC3-Core, LC3-NS3, LC3-NS4B, LC3-NS5A, LC3-NS5B or LC3-P62 (positive control) complexes by PLA using appropriate antibodies. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue Interaction signals were counted as described in materials and methods. In A-E, no significant difference in the frequency of PLA signals between JFH1-infected (n = 50) cells compared to uninfected controls (n = 50) indicating undetectable interaction between LC3 and the viral proteins. F. As control, the in situ interaction between LC3 and its natural ligand P62 was measured in both infected and uninfected cells. Interestingly, the incidence of PLA signals in F was significantly higher in JFH1-infected cells compared to uninfected negative controls (N = 50) (P<0.0001, Student’s t-test). Scale bar, 20μm.