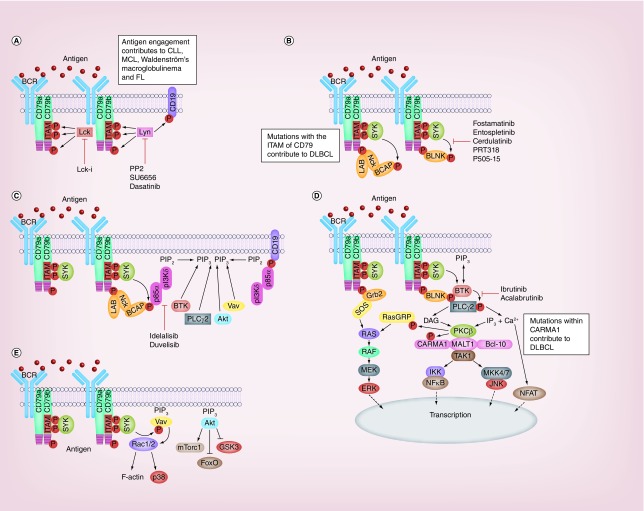
Figure 1. . Signaling pathways of the B-cell receptor, its role in B-cell malignancies and targets of inhibition.
Schematic of the B-cell receptor signaling pathway. (A) Antigen engagement initiates receptor clustering and facilitates Lyn-medated phosphorylation of tyrosines within CD79 and CD19. In chronic lymphocytic leukemia, the SFK Lck mediates phosphorylation of CD79. (B) Syk binds to phospho-tyrosine residues within the ITAM of CD79 and is activated. Adaptor proteins such as BLNK, LAB, NCK, BCAP and Grb2 associate with phospho-tyrosines outside the ITAM on CD79. Proteins such as BLNK and BCAP are substrates of Syk. (C) Phospho-tyrosine residues within BCAP and CD19 attract the regulatory subunit of PI3Kδ leading to the activation of catalytic p110. PI(4,5)P2 is converted to PI(3,4,5)P3 which attracts PH domain containing proteins such as BTK, PLCγ2, Akt and Vav to the plasma membrane. (D) Phospho-tyrosine residues within BLNK act as a scaffold for membrane-associated BTK and PLCγ2, facilitating activation of the former to phosphorate and activate the latter. This catalyzes distal signaling pathway activation leading to NF-κB, JNK and ERK activation. (E) Further distal signals include activation of Vav leading to cytoskeletal rearrangement, and of Akt leading to activation of mTORC1 and inhibition of FoxO.
CLL: Chronic lymphocytic leukemia; DLBCL: Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; FL: Follicular lymphoma; ITAM: Immuno-receptor tyrosine-based activation motifs; MCL: Mantle cell lymphoma.