Figure 2. A common role for KAP1 in repressing ERVs and ZNF genes through H3K9me3.
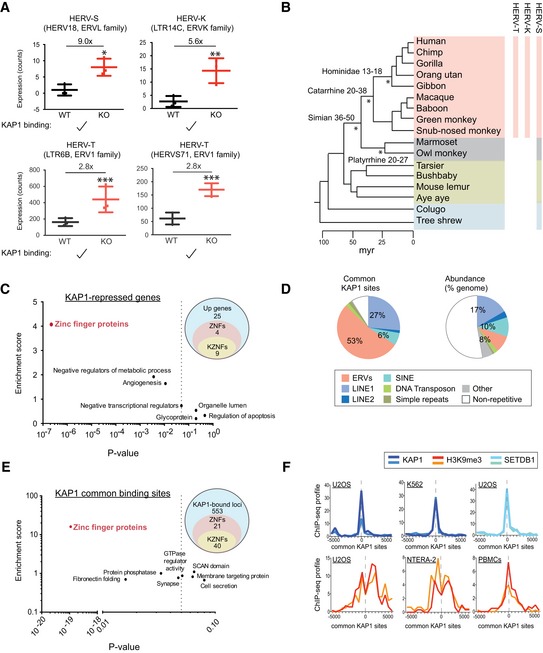
- Boxplots showing repeats significantly upregulated (> 2‐fold where P < 0.05 using DESeq2) in knockout (N = 3) compared to wild‐type (N = 3) HeLa cells based on mRNA‐sequencing data. *P = 0.0174 (HERV‐S), **P = 0.0047 (HERV‐K14C), ***P = 0.00013 (HERV‐T LTR6B), and ***P = 1.90E‐06 (HERV‐T HERVS71). HERV‐T and HERV‐S but not HERVK14C also reached significance when only adjusted P‐values were considered, where differences are compared to the whole of RepBase. KAP1 binding (ENCODE data) is shown in Appendix Fig S1A. All numbers above bars depict fold changes compared to control cells (to one decimal place). Error bars show SD.
- Evolutionary tree showing the age of KAP1‐repressed HERVs identified in (A). Here, HERV‐K refers to HERVK14C. Estimated ages of stated lineages are given and marked with a star. Myr: million years.
- The 38 upregulated genes identified (> 2‐fold where P adj < 0.05) were converted to DAVID IDs and used for gene ontology analysis. Three gene clusters were significantly enriched (P‐value < 0.05, drawn on the plot as a dotted line) in the data set: zinc‐finger proteins (P = 2.2 × 10−7), negative regulators of metabolic processes (P = 0.0036), and angiogenesis (P = 0.011). Venn diagrams on the right show numbers of upregulated genes, ZNFs and KZNFs, and the overlap.
- The 614 KAP1 common binding sites (see Fig EV2D) were interrogated for their nearest gene, and this gene list was converted to DAVID IDs and used for gene ontology analysis. Four gene clusters were significantly enriched (P‐value < 0.05, drawn on the plot as a dotted line): zinc‐finger proteins (P = 1.1 × 10−19), fibronectin folding (P = 0.016), protein phosphatase (P = 0.033), and synapse (P = 0.047). Venn diagrams on the right show numbers of KAP1‐bound loci, ZNFs and KZNFs, and the overlap.
- Genomic coordinates of the common KAP1 sites identified in Fig EV3D were subjected to ChIP‐seq correlation analyses using ChIP‐Cor software (see Materials and Methods). Each plot shows duplicate ChIP‐seq experiments from ENCODE. See Fig EV3B for complete data.
