Figure 6. Model.
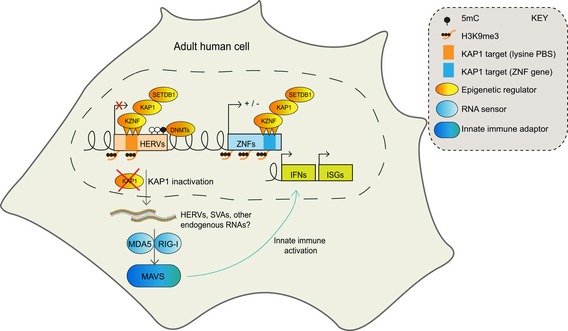
KAP1 regulates ERVs and ZNF genes in differentiated human cells including adult PBMCs and contributes to innate immune control. KAP1 and SETDB1 binding 30 are detected at ERVs and ZNF genes in differentiated cells and overlap with the silent chromatin mark H3K9me3 as well as some cytosine methylation, which we detect at HERVK14C and SVAs. KAP1 inactivation reveals that the KAP1‐KZNF pathway is functionally intact and required in differentiated cells including PBMCs. KAP1 depletion leads to a decrease in H3K9me3 at retrotransposons and to reactivation of HERVs and SVAs. These retrotransposons or potentially other endogenous RNAs produce double‐stranded RNA structures, which activate a type I interferon response through MAVS signaling. KAP1 depletion is not sufficient for global ISG induction, suggesting it exerts partial redundancy at repressing ERVs with other epigenetic mechanisms in differentiated human cells.
