Fig. 3.
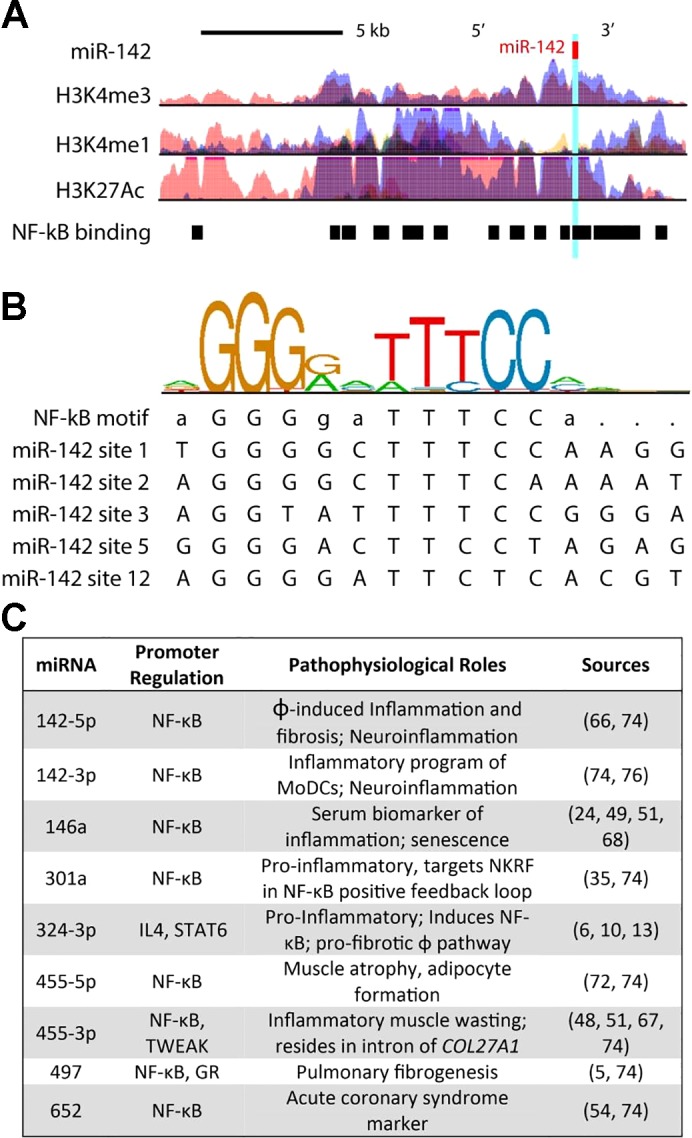
Promoter analysis of miRNAs indicates NF-κB signaling is a shared target of effective drugs. Transcription factor (NF-κB, GR) binding sites and histone (H3) modifications that mark regulatory regions were examined using ChIP-seq data from ENCODE. DNA-binding motifs for each transcription factor were identified through the Factorbook repository. A: schematic of the gene locus for miR-142, illustrating the binding site of 13 neighboring DNA loci that are bound directly by NF-κB. Corresponding epigenetic modification maps are provided showing the location of histone modifications associated with active promoters (H3K4me3) and poised/active enhancers (H3K4me1 and H3K27Ac) in the immediate vicinity of miR-142. B: sequence logo pictogram of base frequency at NF-κB binding sites, with the consensus NF-κB motif provided immediately below. Also provided are five representative NF-κB binding site sequences near miR-142, listed in order from the 5′ to 3′ direction. C: summary of promoter analysis and literature data indicating each miRNA and known factors or conditions associated with its transcriptional regulation. ChIP-seq, chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing; COL27A1, collagen type 27 alpha 1 chain; ENCODE, Encyclopedia of DNA Elements; GR, glucocorticoid receptor; IL4, interleukin 4; MoDCs, monocyte-induced dendritic cells; φ, macrophage; NKRF, NF-κB-repressing factor; STAT6, signal transducer and activator of transcription 6; TWEAK, TNF-like weak inducer of apoptosis.
