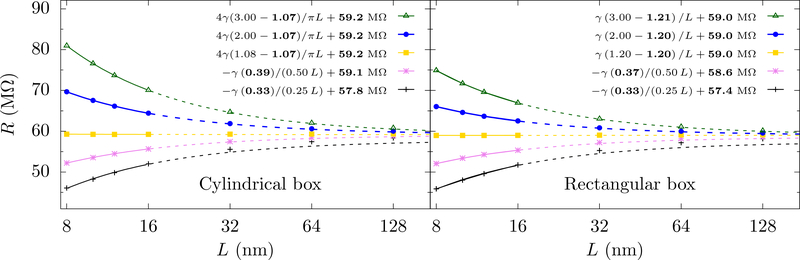
FIG. 3.
Resistance versus L for different aspect ratios α, with a = 1 nm, hp = 1 nm, and γ = 71 MΩ·nm. For small α, dR/dL > 0 and for large α, dR/dL < 0. At special value of α in between – the “golden aspect ratio”, dR/dL = 0 and the resistance is constant (i.e., no finite size effects). Here, the gold line is very close to, but not quite at, the golden aspect ratio. The solid lines show the fits for α>1 and for α < 1, where for cylindrical cells (left panel) and for rectangular cells (right panel). The fit parameters are shown in bold. The dashed lines extrapolate these fits, which match well with the calculations for large L and yield consistent values for R∞. The performance of the scaling analysis using small L indicates that the simulation cell sizes achievable with all-atom MD should be sufficient to find the total resistance (pore plus access). The error of the fits for the f’s and the R∞’s are about 0.5 % and 0.1 %, respectively (except for α = 0.25 where the respective errors are about about 3 % and 0.5 % ).