Figure S2.
Polylysine-Coated Beads Induce Presynaptic Differentiation through Nrx, and Pleiotrophin Binds Nrx, Related to Figure 1
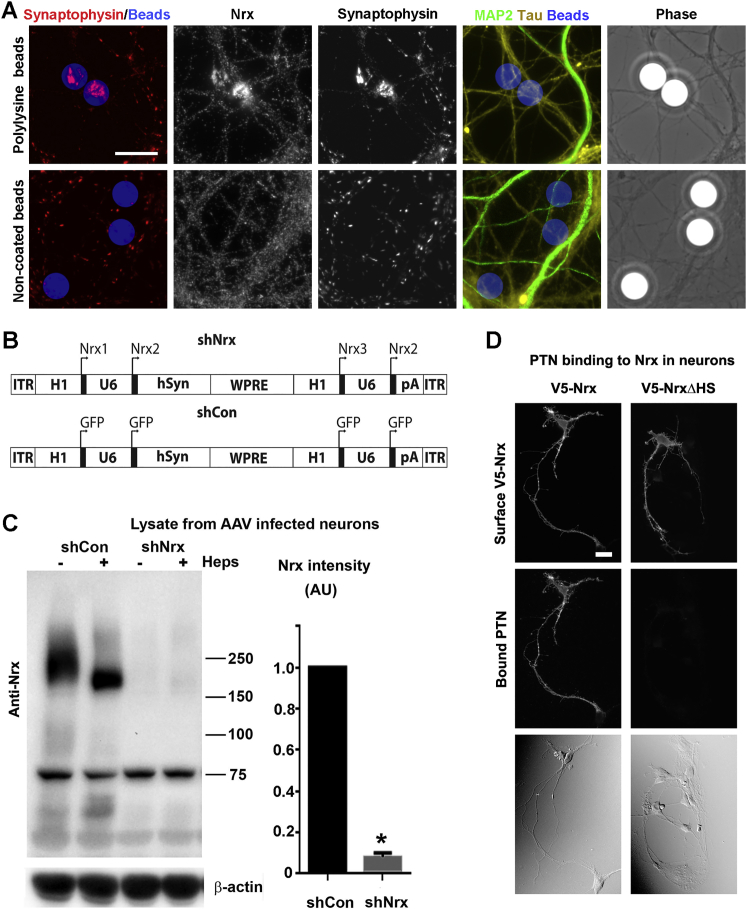
(A) Polylysine-coated beads but not uncoated beads induced clustering of Nrx and of presynaptic marker synaptophysin at contact sites with tau-positive axons; see Figures 1L and 1M for quantitation. Regions of MAP2-positive dendrite contact were excluded from the quantitation to exclude native synapses. For the experiments here and in Figures 1K–1M, beads were added to neuron cultures at 13 DIV and analysis performed at 15 DIV. Scale bar, 10 μm.
(B) The components of the DNA packaged between the inverted terminal repeats (ITRs) in the AAV vector are shown. shNrx consisted of a cassette of shRNAs against rat Nrx1, Nrx2 (duplicated) and Nrx3, regions common to all isoforms, driven by H1 or U6 promoters, plus a human synapsin promoter (hSyn) and Woodchuck Hepatitis Virus posttranscriptional regulatory element (WPRE; we did not test whether the hSyn and WPRE are necessary). In shCon, the Nrx shRNAs were all replaced by shRNA against GFP.
(C) Western blot of lysate from cultured rat hippocampal neurons exposed from 3 to 14 DIV with shCon or shNrx AAV. Parts of the samples were treated with heparinase to condense the Nrx bands. The band just above 75 kDa was presumed to be non-specific. Estimated knockdown efficiency of Nrx α and β combined was 92.1%; ∗p < 0.0001, t test, n = 3. Error bars represent SEM.
(D) Recombinant pleiotrophin (PTN) bound to immature neurons expressing V5-Nrx but not V5-NrxΔHS; see Figure 1N for quantitation. Immature neurons were used because Nrx is not well modified in cell lines and the low levels of native Nrx were insufficient to mediate detectable binding to untransfected cells. Scale bar, 20 μm.