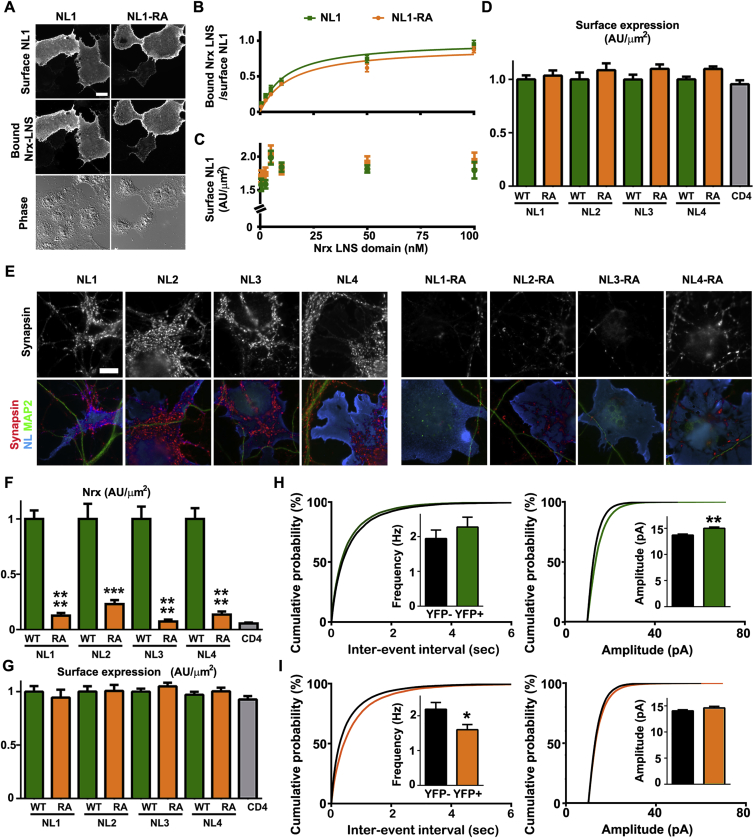
Figure S5.
NLs and LRRTM2 Bind to HS for Synaptic Development, Related to Figure 5
(A-C) The RA mutations on NL1 do not affect its binding to the Nrx LNS domain. Recombinant Nrx LNS ectodomain bound to NL1-RA as well as to wild-type NL1 expressed on the surface of COS7 cells (A). Scatchard analysis of this cell-based binding revealed no significant difference (p > 0.1; B). The level of surface expression of NL1 did not differ among all groups at the different concentrations of ligand (C).
(D and E) RA mutation of NLs 1-4 impairs their ability to induce presynaptic differentiation. In the co-culture assay, clustering of presynaptic marker synapsin in contacting axons was induced well by all NL wild-type on COS7 cells (left two columns), but poorly by the RA mutants (right two columns); see Figure 5F for quantification. Surface expression of NLs in the co-culture experiment did not differ between wild-type and the RA mutant (E).
(F and G) Recruitment of native Nrx in contacting axons induced by each NL on COS7 cells was impaired by the RA mutations. ∗∗∗p < 0.001 and ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001 by Kruskal-Wallis and Dunn’s tests comparing NL RA with WT, n = 28-37 cells from 3 independent experiments. NL RA mutants did not differ significantly from CD4 control. Surface expression of NLs in the co-culture experiment did not differ between wild-type and the RA mutant (G).
(H and I) The raw mEPSC data from Figures 5M and 5N is presented here. ∗p < 0.05 and ∗∗p < 0.01 by Mann-Whitney test, n = 19-24 cells per condition.
Error bars represent SEM. Scale bar: (A) 20 μm, (E) 10 μm.