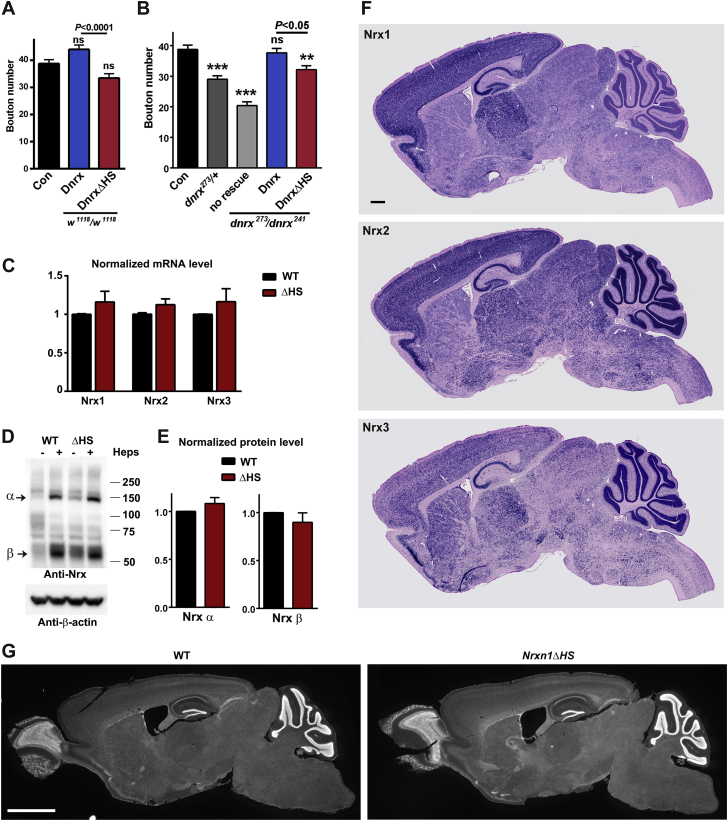
Figure S6.
Nrx HS Modification Is Required for its Function in Vivo, Related to Figure 6
(A and B) Similar to the findings at larval muscle 6/7 (Figure 4), transgenic overexpression of Dnrx resulted in increased bouton number relative to Dnrx HS at larval muscle 4 neuromuscular junctions (A). Dnrx mutants showed reduced numbers of synaptic boutons (B). Bouton number was rescued by neuronal transgenic expression of Dnrx but not DnrxΔHS. ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, and ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001 by ANOVA and Bonferroni tests; n = 17-19 (A), 17-31 (B). Full genotypes are as follows. Con = w1118. Dnrx overexpression = Elav-Gal4; UAS-Dnrx. DnrxΔHS overexpression = Elav-Gal4; UAS-DnrxΔHS. dnrx273/dnrx241 no rescue = Elav-Gal4; dnrx273/dnrx241. dnrx273/dnrx241 Dnrx rescue = Elav-Gal4; UAS-Dnrx; dnrx273/dnrx241. dnrx273/dnrx241 DnrxΔHS rescue = Elav-Gal4; UAS-DnrxΔHS; dnrx273/dnrx241.
(C) As assessed by quantitative PCR from whole brain, neurexin mRNA levels were not significantly altered in Nrxn1ΔHS relative to WT mice (n = 4-5 mice each).
(D and E) Mouse brain crude synaptosome fractions were treated with heparinase (Heps) to condense the major Nrx α and β forms (arrows) and processed by western blot (D). Levels of total Nrx α and β were estimated from these major bands relative to the β-actin loading control. Nrx α and β levels were not significantly altered in Nrxn1ΔHS relative to WT mice (E, n = 3 mice each).
(F) In situ hybridization of WT P14 mouse brain showing overlapping expression patterns of neurexins.
(G) Gross brain morphology was not obviously different in adult Nrxn1ΔHS relative to WT mice as assessed by DAPI nuclear staining.
Error bars represent SEM. Scale bar: (F) 500 μm, (G) 2 mm.