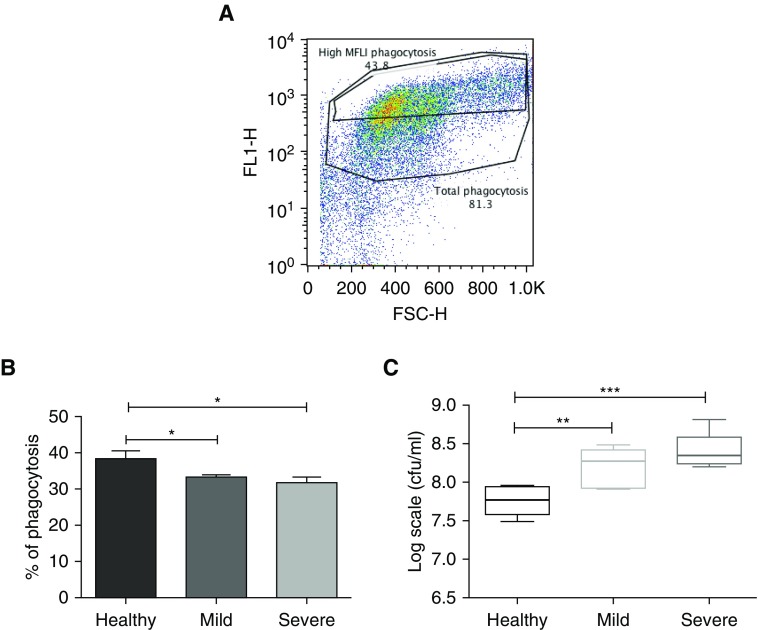
Figure 4.
Impaired bacterial phagocytosis and killing by blood neutrophils from patients with bronchiectasis compared with in healthy control subjects. Blood neutrophils were isolated and cocultured with autologous serum-opsonized GFP (green fluorescent protein)-labeled Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 (at a concentration of 108/ml) for 15 minutes. Bacterial phagocytosis was measured by flow cytometry and serial dilutions of lysed cells were plated on Pseudomonas isolation agar, with colony-forming units counted 24 hours after plating to assess killing. (A) Representative flow cytometry plot of phagocytosis, with high mean fluorescence intensity (MFLI). Gates distinguish total cells having phagocytosed GFP-labeled bacteria, with “High MFLI Phagocytosis” indicating cells that had phagocytosed the most bacteria. (B) Pooled % neutrophil phagocytosis data, showing means ± SEM of n = 8 per group for high MFLI gating. (C) Pooled bacterial killing in log scale units cfu/ml, data, showing median with interquartile range of n = 8 per group. (B and C) One-way ANOVA with Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons used for both experiments, with P values representing the comparison of severe and mild bronchiectasis with healthy volunteers (used as control). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. FL1-H = fluorescence index–height; FSC-H = forward scatter–height.