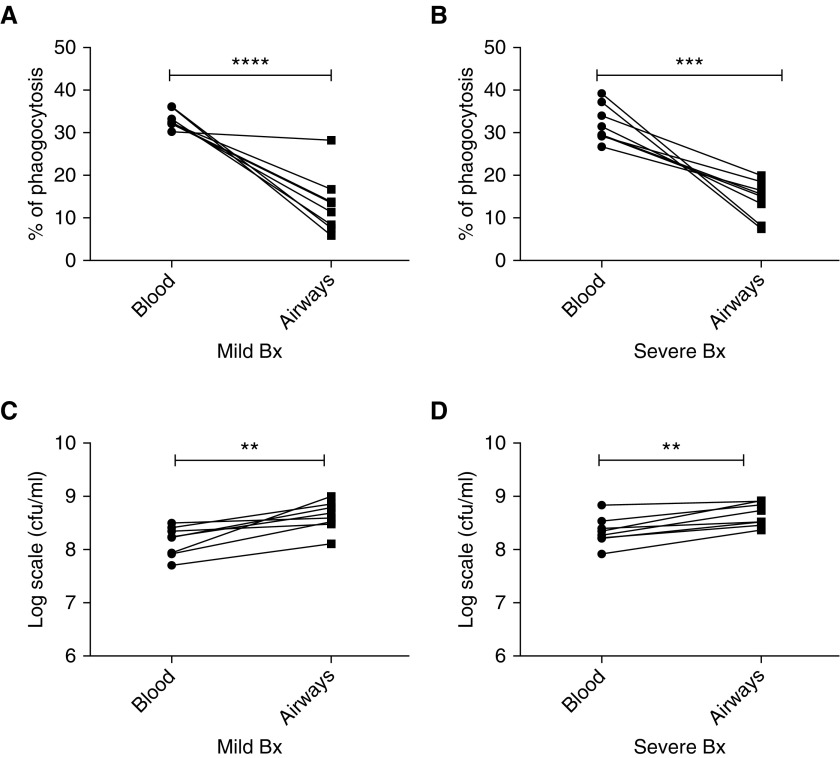
Figure 5.
Impaired antibacterial function of BAL-derived neutrophils compared with matched blood neutrophils from patients with mild and severe bronchiectasis. Neutrophils were isolated from BAL and blood from patients with mild and severe bronchiectasis, and cocultured with serum opsonized green fluorescent protein PAO1 for 15 minutes (blood neutrophils) or 60 minutes (BAL neutrophils). Bacterial phagocytosis was measured by flow cytometry, and serial dilutions of lysed cells were plated on Pseudomonas isolation agar, with colony-forming units counted to assess killing. (A) Mild and (B) severe bronchiectasis: matched neutrophil phagocytosis data in blood and BAL-derived neutrophils in the same patient; n = 8 per group. (C) Mild and (D) severe bronchiectasis: matched bacterial killing in log scale units cfu/ml, in blood and BAL-derived neutrophils in the same patient; n = 8 per group. Two-way ANOVA showed no significant difference in the antibacterial activity between mild and severe bronchiectasis; P = 0.2. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001. Bx = bronchiectasis.