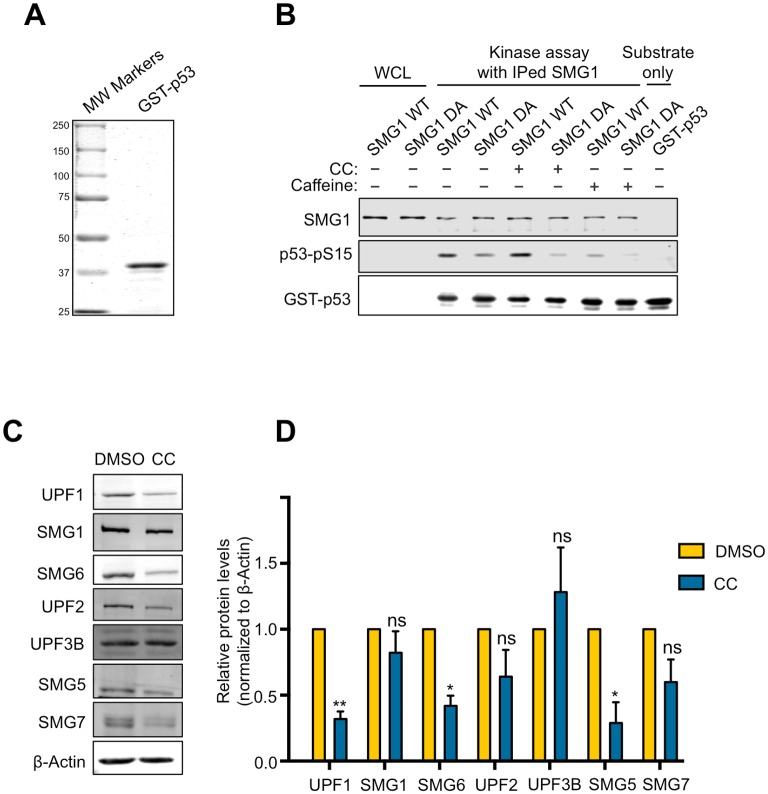
Fig 4. CC reduces protein levels of multiple NMD factors, but does not inhibit SMG1 kinase activity.
A. Purified, recombinant GST-p53 protein containing a N-terminal fragment of p53. B. Result of in vitro kinase assay for SMG1 with GST-p53 as substrate containing the phosphorylation site S15. CC (10 μM) was used to test effects on SMG1 kinase activity. Caffeine (10 mM), a known inhibitor of SMG1, was used as a positive control. C. Effects of CC on the protein levels of NMD factors UPF1, UPF2, UPF3B, SMG1, SMG5, SMG6, and SMG7 in U2OS reporter cells. D. Quantification of the effects of CC on the protein levels of NMD factors UPF1, UPF2, UPF3B, SMG1, SMG5, SMG6, SMG7. Quantification was performed by measuring signal intensity relative to actin. Protein levels of DMSO-treated cells are normalized to 1. Data represent the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. **p ≤ 0.01; *p ≤ 0.05; ns, not significant (paired t-test).