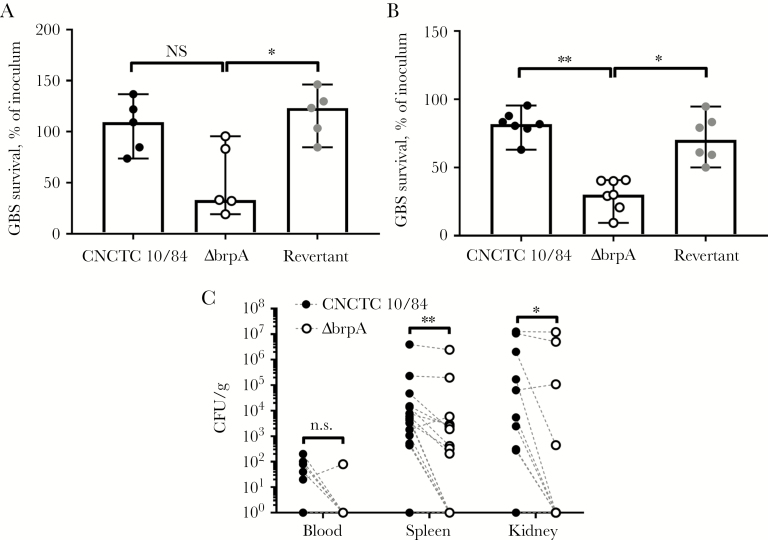
Figure 5.
Biofilm regulatory protein A (BrpA)–deficient group B Streptococcus (GBS) is more susceptible to killing by murine whole blood and neutrophils and is attenuated in an in vivo sepsis model. Murine whole blood (A) or peritoneal-derived leukocytes (85% neutrophils; B) killing of wild-type (WT), ΔbrpA, and revertant strains, expressed as a percentage of the inoculum. Biological replicates (n = 5–7) are shown, with lines indicating median values ± 95% confidence intervals. C, In a competition model, CD1 mice were infected intraperitoneally with 1 × 107 colony-forming units (CFU) of WT and ΔbrpA strains (2 × 107 CFU total/mouse), and bacterial burdens were quantified 24 hours after infection. Symbols represent biological replicates (n = 15), and paired values (WT and ΔbrpA CFU) from each mouse are connected with dashed lines. Data were analyzed using the Kruskal-Wallis test with the Dunn multiple comparisons test (A and B) and the 2-tailed Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test with Spearman rank-order correlation (C). **P < .01 and *P < .05. NS, not significant.