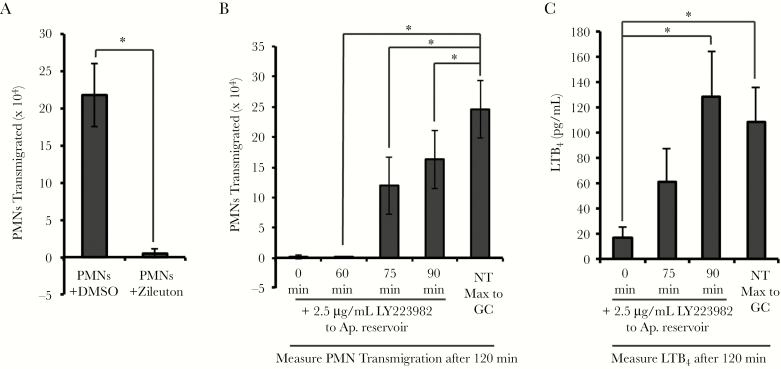
Figure 3.
Neutrophils produce leukotriene B4 (LTB4) to amplify neutrophil transepithelial migration to Neisseria gonorrhoeae (GC). A, Primary human neutrophils were pretreated with the 5-lipoxygenase inhibitor Zileuton (25 μM) or vehicle (dimethyl sulfoxide) prior to assaying neutrophil transepithelial migration across polarized human End1/E6E7 (End1) monolayers infected with GC at a multiplicity of infection = 10 for 1 hour. B, LY223982 (2.5 μg/mL), an antagonist to the high-affinity LTB4 receptor BLT1, was added to the apical reservoir of infected End1 monolayers at the indicated time points during neutrophil transmigration (0, 60, 75, and 90 minutes). Neutrophil transmigration after addition of LY223982 is compared to the maximum migration seen to apical GC infection after 120 minutes with no treatment. C, Supernatants from apical and basolateral compartments following GC infection and/or neutrophil transepithelial migration were collected at the indicated time points and conditions and passed through a 0.2-μm filter, and LTB4 was quantified by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Results are expressed as a mean ± standard error of the mean for at least 3 independent experiments per condition. Statistics for were calculated using a 2-tailed, unpaired (A and B) or paired (C) Student t test. *P < .05. Abbreviations: Ap., apical; DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide; GC, Neisseria gonorrhoeae; LTB4, leukotriene B4; NT, no treatment; PMN, polymorphonuclear cell/neutrophil.