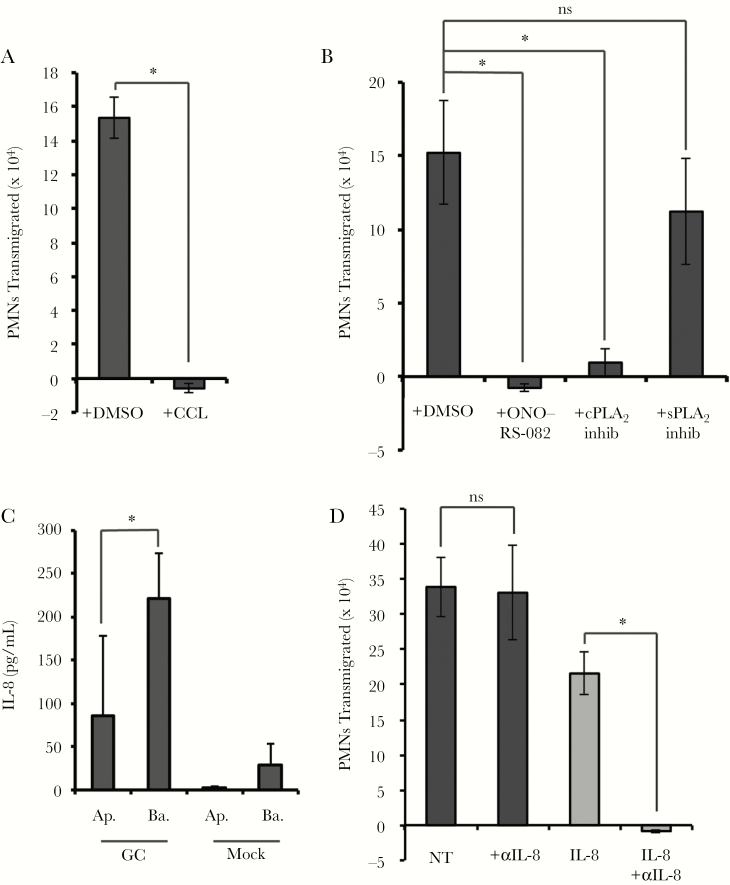
Figure 4.
Neutrophil transepithelial migration to Neisseria gonorrhoeae (GC) requires an epithelial pathway involving protein kinase C and phospholipase A2 (PLA2), but not apically directed interleukin 8 (IL-8). For treatment with inhibitors of epithelial cell targets, epithelial cells were pretreated with the inhibitor and then washed thoroughly before infection with GC at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) = 10 and neutrophil transepithelial migration. Polarized human End1/E6E7 (End1) monolayers were pretreated with the pan–protein kinase C inhibitor chelerythrine chloride (CCL) (5 μM) (A), or the pan-PLA2 inhibitor ONO-RS-082 (5 μM), cytosolic PLA2α inhibitor (cPLA2 inhib) (6 μM), or soluble PLA2 inhibitor 2,4ʹ-dibromoacetophenone (sPLA2 inhib) (7 μM) (B). C, Supernatants from apical and basolateral compartments following a 3-hour GC infection or mock infection were collected and passed through a 0.2-μm filter, and IL-8 was quantified by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. D, Polarized End1 monolayers were infected with GC at an MOI = 10 for 1 hour. During neutrophil transepithelial migration, an IL-8 blocking antibody (20 μg/mL), was added to the apical and basolateral reservoirs immediately prior to addition of neutrophils. Gray bars represent neutrophil transepithelial migration to an imposed apical gradient of IL-8, and black bars represent neutrophil migration to GC. Results are expressed as mean ± standard error of the mean for at least 3 independent experiments per condition. Statistics were calculated using a 2-tailed, unpaired (A, B, and D) or paired (C) Student t test. *P < .05. Abbreviations: Ap., apical; Ba., basolateral; CCL, chelerythrine chloride; cPLA2, cytosolic phospholipase A2; DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide; GC, Neisseria gonorrhoeae; IL-8, interleukin 8; inhib, inhibitor; ns, not significant; NT, no treatment; PMN, polymorphonuclear cell/neutrophil; sPLA2, soluble phospholipase A2.