Figure 2. Expression of human FXI in F9- and F11−/− mice by hydrodynamic tail vein injection.
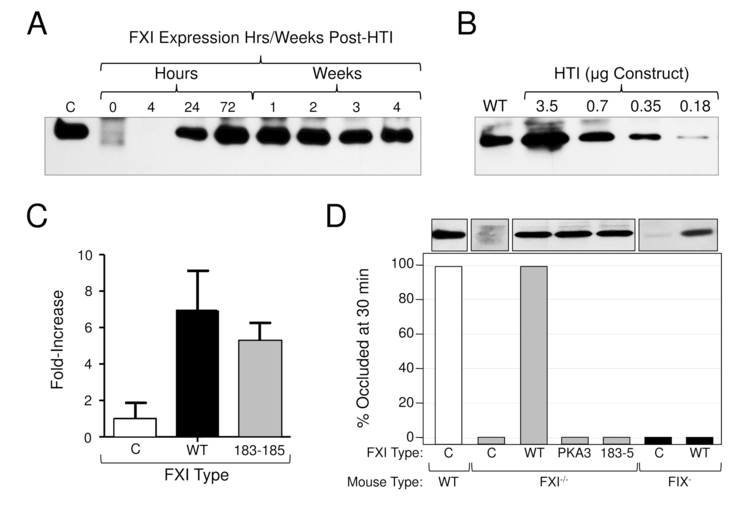
(A) HTI in F11−/− mice - duration of expression. Shown is a western blot of 1 μl samples of mouse plasma at various times after HTI with a Human FXI/ EEV600A construct (3.5 μg). C (control) is a 100 ng sample of purified human FXI. (B) HTI in F11−/− mice - dose effect. Shown is a western blot of 1 μl samples of mouse plasma 24 hrs after HTI with varying concentrations of human FXI/ EEV600A construct. WT indicates a sample of plasma from a normal mouse. (C) Expression of human FXI in F9−/− mice undergoing testing in the saphenous vein bleeding model. Fold-increase in plasma FXI level as determined by densitometry evaluation of western blots. Results for FXI-WT and FXI-Ala183–185 are shown relative to the average value for mice treated with empty vector, which was assigned a value of 1. The value for empty vector control reflects endogenous FXI in F9- mice. Results are +/− 1 SD. (D) Effect of FXI-WT and FXI-Ala183–185 in a carotid artery thrombosis model in F11−/− and F9- mice. Shown are the percent of F11−/− and F9- mice tested in a FeCl3-carotid artery thrombosis model with occluded carotid arteries 30 minutes after vessel injury. Twenty-four hours prior to testing, F11−/− mice (gray bars) underwent HTI with empty vector (C) or with vectors containing cDNAs for wild type human FXI (WT) or FXI-Ala183–185 (183–5). Also shown are results for mice expressing FXI containing the A3 domain of prekallikrein (PKA3), like FXI-Ala183–185, removes the FIX-binding site on FXIa. F9- mice (black bars) underwent HTI with empty vector (C) or vector containing cDNA for wild type human FXI (WT). Results for wild type mice (white bar) are shown for comparison. For each bar n = 6 animals. The western blots at the top of the figure were prepared with 1 μl samples of plasma from representative mice. For all panels, blots were developed with the monoclonal IgG 14E11 [21], which was raised against mouse FXI in a F11−/− mouse, and which recognizes mouse and human FXI.
