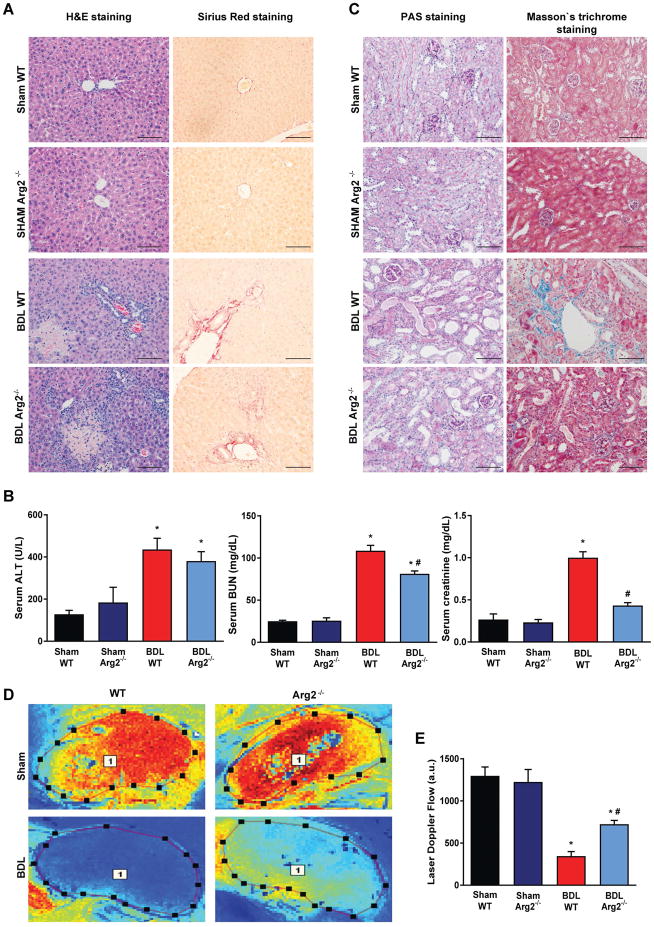
Fig. 6. Arginase-2 deficient mice are partially rescued from kidney injury in bile duct-ligated mice.
(A) Histological assessment of hepatic necrosis, and fibrosis in sham operated wild type (Sham WT) or Arginase-2-deficient mice (Sham Arg2−/−) or in wild type or Arginase-2-deficient mice subjected to bile duct-ligation and sacrificed on postoperative 14 (BDL WT, or BDL Arg2−/−), respectively. Scale bar represent 100 μm. (B) Enzymatic markers of liver and kidney injury. (C) Histological assessment of tubular injury (PAS staining) and tubulointerstitial fibrosis (Masson’s trichrome staining). Scale bar represent 100 μm. (D) Representative illustration of renal microcirculation assessment by Laser speckle contrast analysis. (E) Quantification of renal microvascular flow. Results are mean±S.E.M. *p<0.05 vs. Sham WT #p<0.05 vs. BDL WT, n=4–6.