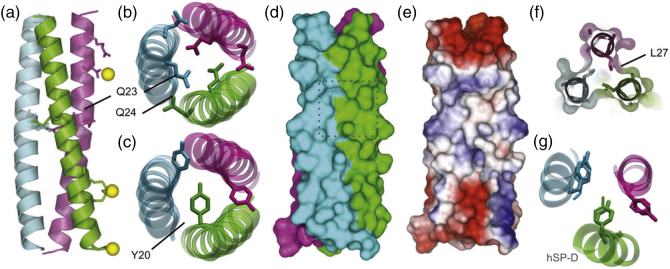
Fig. 2.
FapFCC forms an asymmetric trimeric coiled coil. (a) Overall structure of the periplasmic domain of FapF, FapFCC. FapFCC forms a parallel trimeric coiled coil. Coiled-coil charged surface residues interacting with Zn2 + (yellow spheres) are highlighted for a single chain. Zinc coordination was validated using the checkmymetal server [17] and consistent with molecular simulation data (Fig. S3). (b) Buried Gln23 residues form a hydrogen bond network with interfacial Gln24 of neighboring chains (Q-layer, shown in more detail in Fig. S5). (c) FapFCC contains a single buried Tyr20. (d) The surface of the periplasmic domain highlighting a large hydrophobic cleft in the center of the coil. (e) Surface view colored according to charge to further highlight the hydrophobic cleft. (f) Cutaway view of the hydrophobic cleft indicated in panel D showing the exposed Leu27 side chains. (g) Overlay of the asymmetric tyrosine arrangement of FapFCC (thin lines) with human lung surfactant protein D (PDB ID 1b08 [18]) (thick lines and cartoon). Figures generated using Pymol [19] and VMD [20].