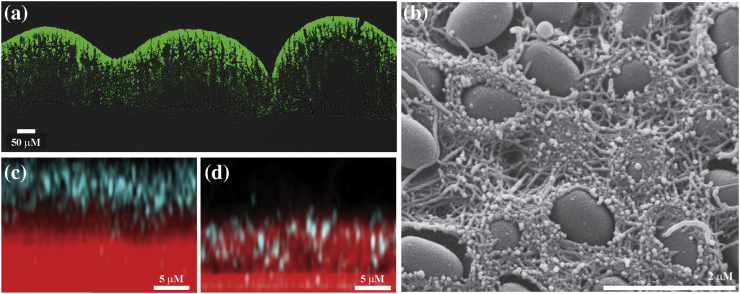
Fig. 2.
A structural and protective role for curli in the E. coli biofilm matrix. (a) The localization of the curli in a vertical cross section of a 7-day-old E. coli biofilm stained with thioflavin S (ThS). Merged bright-field and false-colored fluorescence for ThS. (b) Scanning electron micrograph in high vacuum mode of the top view of a 7-day-old K-12 W3110 cellulose-free E. coli biofilm. The cells are round and the curli baskets are visible. (c, d) Maximum intensity z-projections of phage localization (cyan) after 8-h exposure of 72 h E. coli wild-type (c) and curli-deficient (d) biofilm. Cells are in red. Parts a and b [89] and c and d [7] are reproduced with permission along with the corresponding legend.