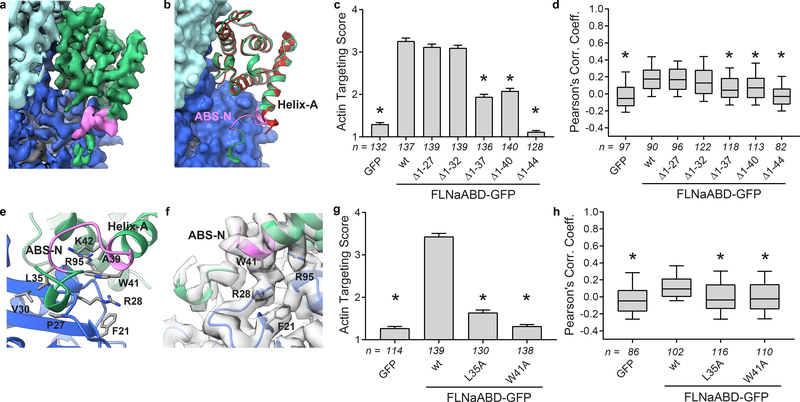
Figure 2. ABS-N contributes to F-actin binding.
a Cryo-EM density depicting ABS-N (residues P29-K43, pink) extending from helix-A of the FLNaCH1 domain (green) alongside actin(n) (dark blue). b Superposition of the refined actin-bound FLNaCH1 and ABS-N (green, pink) cryo-EM structure and the published unbound FLNaCH1 crystal structure PDB 3HOC (red) illustrates the formation of the structured ABS-N upon actin-binding. Actin in surface representation and FLNa in ribbon representation, colored as in (a). c F-actin targeting of wild-type (wt) and N-terminal deletion constructs of FLNaABD-GFP expressed in mouse NIH-3T3 fibroblasts. Bars = mean ± SEM, n = number of scored cells from 3 independent experiments, * significantly different from wt (P<0.001) in a one-way ANOVA (F6,944=211) with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test. d Pearson’s correlation coefficient (PCC) scoring of FLNaABD-GFP co-localization with N-terminal truncations. Center = median, boxes = 25th–50th and 50th–75th percentiles, whiskers extend to 10th and 90th percentiles, n = number of scored cells from 3 independent experiments, * significantly different from wt (P<0.001) in a one-way ANOVA (F6,711=21.63) with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test. e Detailed view of actin-binding by ABS-N with binding residues in stick representation. f Cryo-EM density supports a probable cation-π interaction between FLNa W41 and actin R28. g F-actin targeting of ABS-N-mutant FLNaABD-GFP, scored and graphed as in (c). One-way ANOVA (F3,564=339.9) with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test. h PCC scoring of ABS-N-mutant FLNaABD-GFP, scored and graphed as in (d). One-way ANOVA (F3,410=13) with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test.