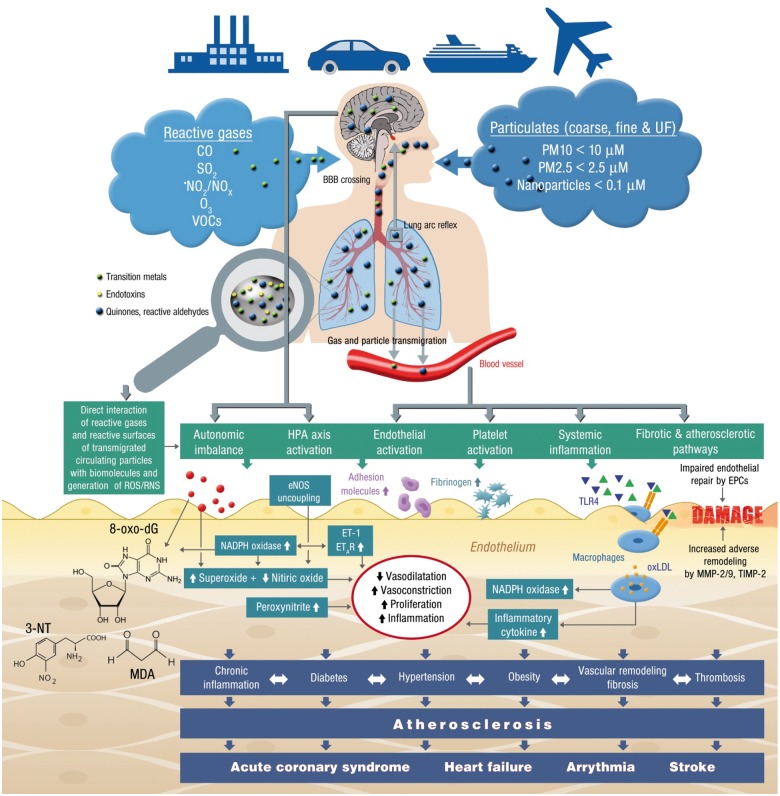
Figure 3.
Summary of pathophysiological mechanisms by which air pollution components such as reactive gases and particulates causes endothelial dysfunction, increased oxidative stress, inflammation and subsequently cardiovascular disease. Green and blue triangles are damage- and pathogen-associated molecular patterns (e.g. free DNA fragments, hyaluronan, 7-ketocholesterol, oxidized 1-palmitoyl-2-arachidonyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphorylcholine, lipopolysaccharide) as well as soluble heavy/transition metals. EPCs, endothelial progenitor cells; ET-1, endothelin-1; ETAR, endothelin type A receptor; HPA axis, hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis; MDA, malondialdehyde; MMP, metalloproteinase; 3-NT, 3-nitrotyrosine; 8-oxo-dG, 8-oxo-deoxyguanosine; TIMP, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases; TLR4, toll-like receptor 4; VOCs, volatile organic compounds.