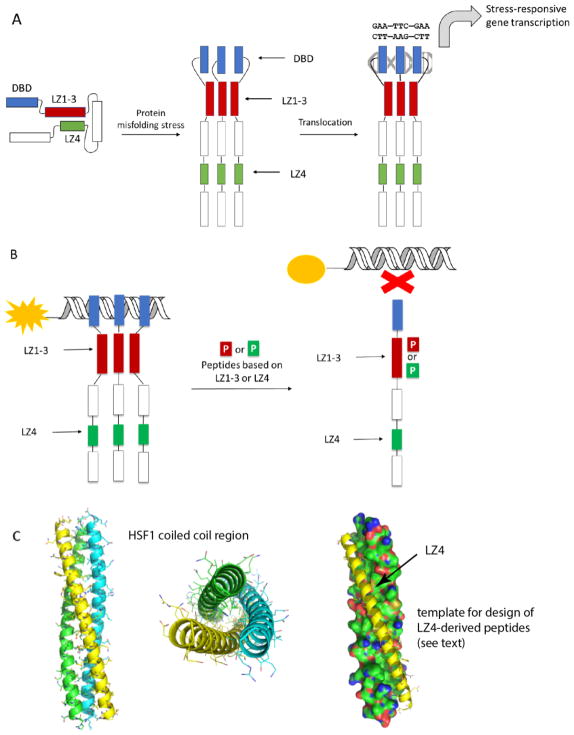
Figure 1.
Structure and molecular mechanisms of HSF1. (A) HSF1 is held in a repressed state through interactions between LZ1-3 and LZ4. A stress response leads to oligomerization and transcriptional activation of heat shock responsive genes. (B) Proposed mechanisms by which LZ1-3 or LZ4 derived peptides might mimic intra-molecular interactions and suppress HSF1 activation. This activity might be detected by a fluorescence polarization (FP) experiment, in which changes in binding of HSF1 to fluorescent HSE is measured. (C) Homology model of human HSF1 LZ1-3 domain homotrimer. Coiled-coils are shown in cartoon form (left and middle), while the peptide template for LZ1-3 ligand design is shown as a yellow cartoon (right).