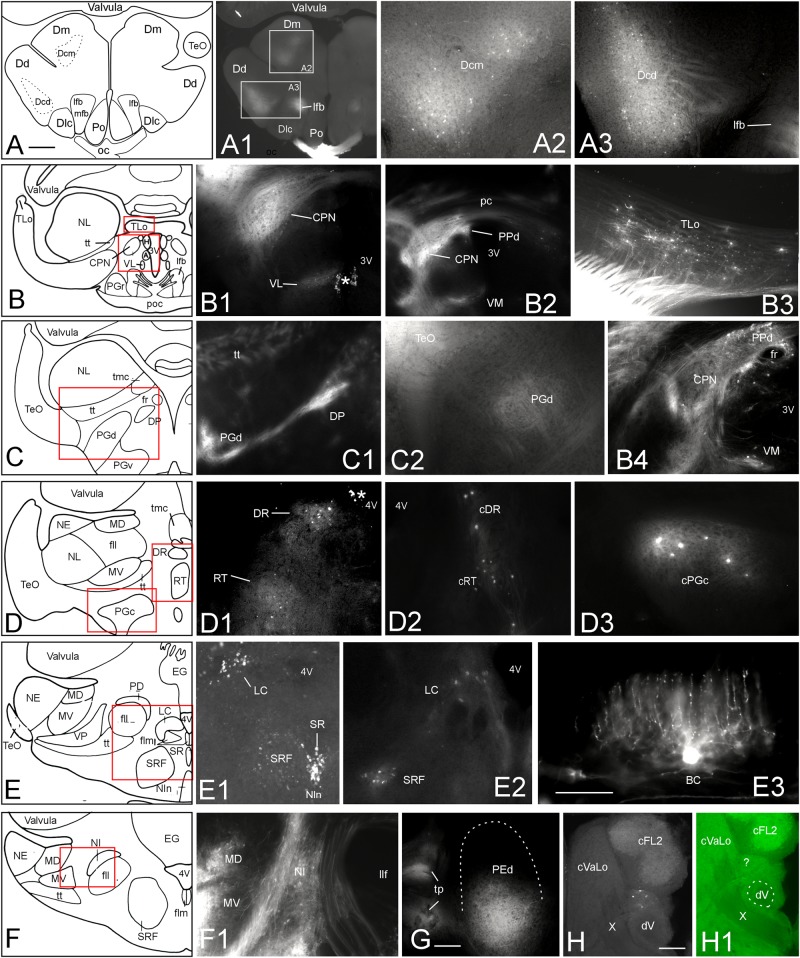
FIGURE 6.
Additional tectal connections after DiI injections into the optic tectum of Gnathonemus petersii. Generally, connections are ipsilateral and lateral is to the left. Contralaterally labeled structures are indicated with prefix “c”. (A–F) Drawings of brain cross sections with areas shown in microphotographs (A1) through (F1) highlighted by red or white rectangles. (A1,A2) Telencephalic level caudal to anterior commissure. (A2) Medial part of central zone of dorsal telencephalon. (A3) Dorsal part of central zone of dorsal telencaphalon. (B1) Central pretectal nucleus (CPN) and ventrolateral thalamic nucleus (VL). (B2) Central and dorsal periventricular pretectal and ventromedial thalamic nuclei. (B3) Torus longitudinalis. (B4) Central and dorsal periventricular pretectal and ventromedial thalamic nuclei with emphasis on retrogradely labeled cells. (C1) Dorsal preglomerular and dorsal posterior thalamic nuclei. (C2) Dorsal preglomerular nucleus. (D1) Dorsal reticular and rostral tegmental nuclei. (D2) Same nuclei contralaterally. (D3) contralateral caudal preglomerular nucleus. (E1) Superior raphe, superior reticular formation and Locus coeruleus. (E2) Locus coeruleus and superior reticular formation. (E3) Valvular basal efferent cell. Note extensive dendritic tree. (F1) Nucleus isthmi and mediodorsal and medioventral toral nuclei. (G) Dorsal pre-eminential nucleus. (H) Labeled neurons ventral to cFL2 and lateral to vagal lobe. Note that this section level is indicated in Figure 8Q. (H1) Microphotograph as (H) in green epifluorescence to highlight entrance of vagal nerve. Asterisk: artifact. Size bar in (A): 0.5 mm, applies to (A1) and (B) through (F). Size bars in (E3,G,H): 0.25 mm. See text for details. A, anterior thalamic nucleus; BC, basal (efferent cerebellar) cell; cDR, contralateral DR; cFL2, contralateral lateral funicular nucleus 2; cPGc, contralateral PGc; CPN, central pretectal nucleus; cRT, contralateral RT; cVaLo, contralateral vagal lobe; dV, descending trigeminal root; Dcd, Dcm, dorsal and medial parts of central zone of dorsal telencephalon; Dd, dorsal zone of dorsal telencephalon; Dlc, part c of lateral zone of dorsal telencephalon; Dm, medial zone of dorsal telencephalon; DP, dorsoposterior thalamic nucleus; DR, rostrodorsal tegmental nucleus; EG, eminentia granularis; fll, lateral longitudinal fascicle; flm, medial longitudinal fascicle; fr, fasciculus retroflexus; H, habenula; LC, locus coeruleus; lfb, lateral forebrain bundle; MD, mediodorsal nucleus of torus semicircularis; mfb, medial forebrain bundle; MV, medioventral nucleus of torus semicircularis; NE, exterolateral nucleus of torus semicircularis; NI, nucleus isthmi; Nln, nucleus interpeduncularis; NL, lateral nucleus of torus semicircularis; oc, optic chiasma; pc, posterior commissure; PD, dorsal perilemniscal part of nucleus lateralis valvulae; PEd, dorsal pre-eminential nucleus; PGc, PGd, PGr, PGv caudal, dorsal, rostral, ventral preglomerular nuclei; Po, preoptic region; poc, postoptic commissure; PPd, dorsal periventricular pretectal nucleus; RT, rostral tegmental nucleus (of Grover and Sharma, 1981); SR, superior raphe; SRF, superior reticular formation; TeO, tectum opticum; TLo, torus longitudinalis; tmc, mesencephalo-cerebellar tract; tp, tecto-pre-eminential tract; tt, toro-pre-eminential tract; VL, VM ventrolateral, ventromedial thalamic nucleus; VP, ventroposterior nucleus of torus semicircularis; X, vagal nerve; 3V, third ventricle; 4V, fourth ventricle.