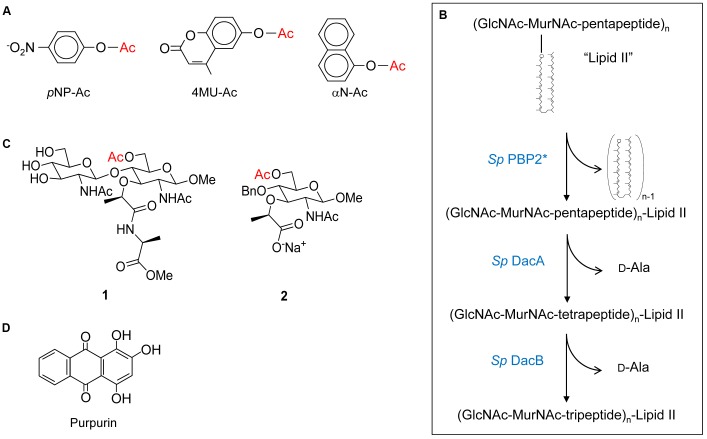
FIGURE 4.
Structures of substrates and inhibitors of PG O-acetyltransferases and O-acetylesterases. (A) Chromogenic p-nitrophenyl acetate (pNP-Ac) and fluorogenic 4-methylumbelliferyl acetate (4MU-Ac) and α-naphthyl acetate (αN-Ac) as substrates for detection of esterase activity. (B) Production of Lipid II-based polymers as substrates for O-acetyltransferase activity. Polymerization of Lipid II by PBP2 from S. pneumoniae produces homopolymers of GlcNAc and MurNAc with associated pentapeptides, and the concomitant release of all but the terminal bactoprenol (undecaprenyl) residues. Successive hydrolytic reactions with the carboxypeptidases DacA and DacB (both also from S. pneumoniae) generate homopolymers with associated tetrapeptides and tripeptides, respectively. (C) Structures of synthetic N,O-diAc-MurN-based substrates (compounds 1 and 2) for analysis of Ape activity. (D) Structure of the Ape inhibitor purpurin.