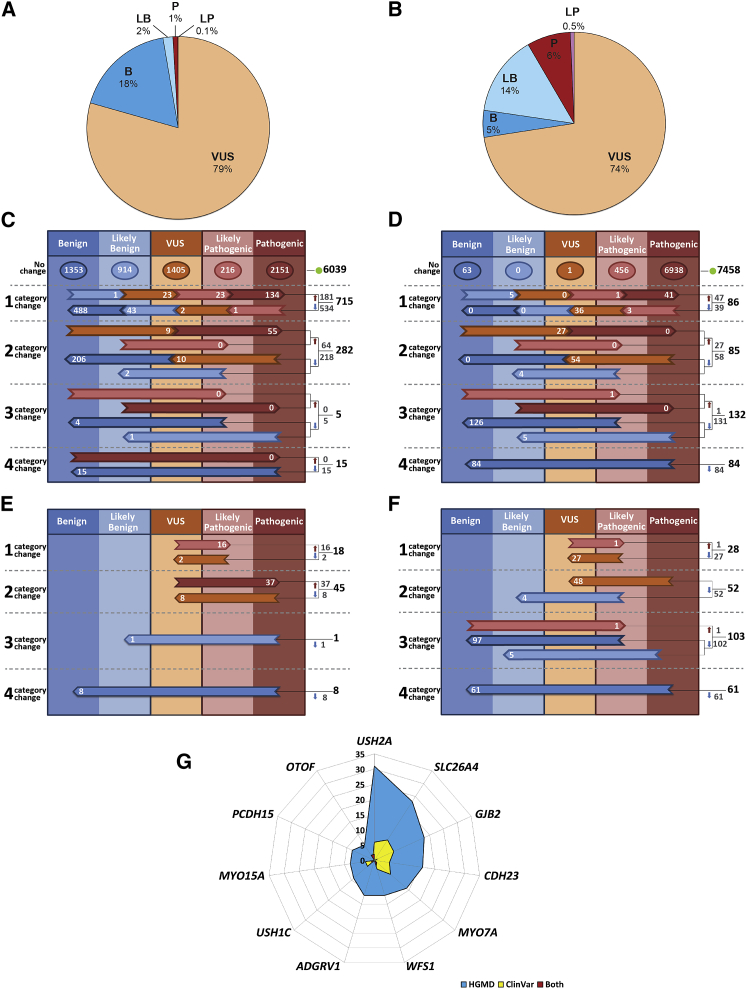
Figure 2.
Variant Classification by the DVD
(A) Fractions of different classification categories for variants in the whole DVD.
(B) A slightly different picture emerges when only clinically relevant regions and deafness-associated variants (variants that were associated with other non-related deafness phenotypes are excluded) are considered.
(C) Comparative overview of DVD versus ClinVar. 7,056 classifications from ClinVar were identified within our specified gene regions (each variant in ClinVar with multiple submissions for pathogenicity has been represented by its most pathogenic submission). Of this number, 6,039 ClinVar classifications agreed with the corresponding DVD classification whereas there was disagreement for 1,017 variants.
(D) Comparative overview of DVD versus HGMD. 7,845 classifications from HGMD were identified within our specified gene regions. Of this number, 7,458 classifications agreed with the corresponding DVD classification and discrepancies were found for 387 variants.
(E) There were 72 major categorical changes between ClinVar and DVD that resulted in medically significant differences (53 up-classifications and 19 down-classifications).
(F) 244 medically significant reclassifications were found when DVD was compared to HGMD (2 up-classifications and 242 down-classifications).
(G) Of the 20% of genes carrying the greatest numbers of medically significant changes, 6 are implicated in Usher syndrome.
For (C) through (F), the horizontal arrows show discordant calls, with the number of discordant classifications shown within each arrow; totals are listed to the right of the colored columns.