Fig. 1.
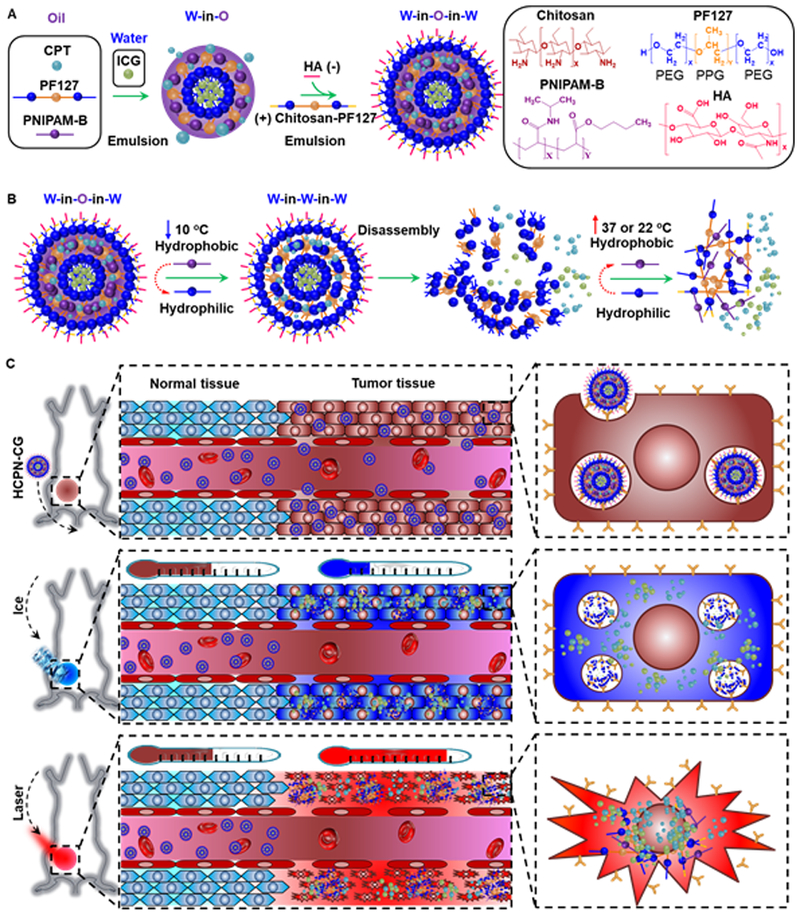
Synthesis and mechanism of cold-responsive nanoparticle for drug delivery to treat cancer. (A) Hyaluronic acid (HA or H), chitosan-modified Pluronic F127 (chitosan-PF127 or C), PF127 (P), and poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-butylacrylate) (PNIPAM-B or N) were used to prepare the irinotecan (CPT or C) and indocyanine green (ICG or G)-laden HCPN-CG nanoparticles using the double-emulsion method. (B) The thermal phase transition behavior of PNIPAM-B from being water-insoluble to highly water-soluble can cause disassembly of the HCPN-CG nanoparticles upon cooling to below room temperature, which can result in burst release of the encapsulated drug. (C) In vivo accumulation of HCPN-CG nanoparticles in tumor through the enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect of tumor vasculature, burst drug release upon cooling with ice, and enhanced antitumor efficacy with ice cooling followed by near infrared (NIR) laser irradiation.
