Fig. 3.
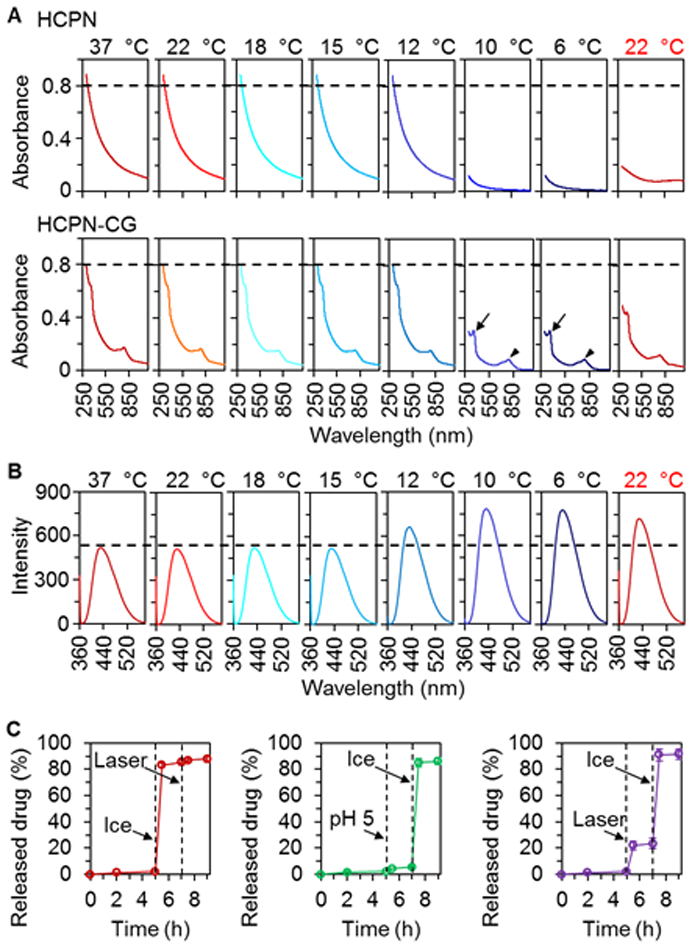
Characterization of cold-responsive drug release from HCPN-CG nanoparticles. (A) UV-Vis absorbance of HCPN (top) and HCPN-CG (bottom) nanoparticles at different temperature showing the cold-responsive ability of HCPN-CG nanoparticles. Arrow and arrowhead indicate the absorbance peaks of CPT and ICG, respectively. (B) Fluorescence emission spectra of HCPN-CG nanoparticles at various temperatures showing cold-triggered release of CPT. (C) A comparison of the triggered release of CPT from HCPN-CG nanoparticles by ice cooling (5 min), acidic pH (5.0, 5 min), and NIR laser irradiation (1 W/cm2, 5 min), showing the cold-triggered drug release from HCPN-CG nanoparticles is much more effective than the other two treatments. Moreover, the efficient drug release triggered by cold is not affected by pre-treatment with the NIR laser or low pH. Error bars represent ± S.D. (n = 3).
