Figure 5.
TRPC1 Deficiency Results in Reduced IFNγ-Induced Phosphorylation of STAT1 and NF-κB as well as Impaired Production of M1 Inflammatory Mediators in Peritoneal Macrophages In Vivo
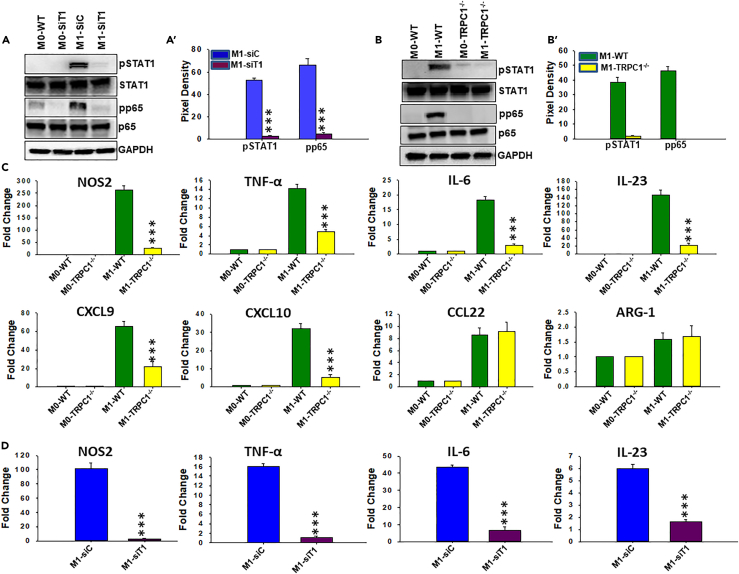
Immunoblotting and qRT-PCR analysis were performed on peritoneal macrophages from IFNγ i.p.-injected WT and TRPC1−/− mice. IFNγ-induced effect was also analyzed in peritoneal macrophages in which TRPC1 was transiently knocked down in vivo by i.p. injection of TRPC1 siRNA before the animals received IFNγ.
(A) Peritoneal macrophages transiently deficient in TRPC1 or control cells from mice that received siRNA specific for TRPC1 or non-targeting siRNA were harvested 24 hr after i.p. injection with vehicle (M0-siC, M0-siT1) or IFNγ (M1-siC, M1-siT1). Western blot analysis using anti-pSTAT1, pp65, p65, STAT1, and anti-GAPDH was performed on equal amount of the respective cell lysates. The bar graph (A′) depicts average ± SEM of pixel intensity of the pSTAT1 and pp65 protein bands.
(B) Immunoblots of pSTAT1 and pp65 levels in peritoneal macrophages from PBS- (M0) or IFNγ (M1)-injected WT and TRPC1−/−mice. The bar graph (B′) depicts averages ±SEM of pixel intensity of the pSTAT1 and pp65 protein bands.
(C) The expression of M1-associated inflammatory mediators and M2-specific anti-inflammatory mediators measured by qRT-PCR in peritoneal macrophages from PBS- (M0) or IFNγ (M1)-injected WT and TRPC1−/−mice.
(D) The expression of M1-associated inflammatory mediators in M0 and M1 peritoneal macrophages from PBS- (M0) or IFNγ (M1)-injected mice measured by qRT-PCR after in vivo treatment with siC or siT1 RNA, detailed in (A).
***p ≤ 0.001 (Student's t test).
See also Figure S8.