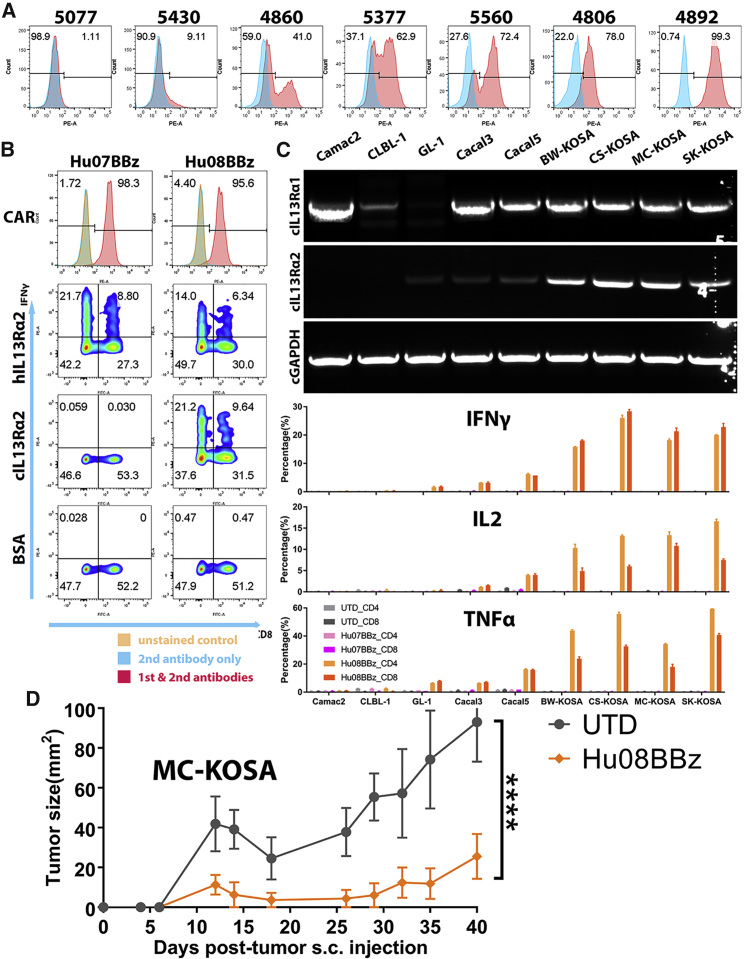
Figure 5.
IL-13Rα2 CAR T Cells Respond to Canine Tumors
(A) IL-13Rα2 expression analysis on the patient-derived glioma stem cell lines (5077, 5430, 4860, 5377, 5560, 4806, and 4892) with isotype antibody staining control in blue. (B) CAR expression was detected on the mRNA-electroporated IL-13Rα2-targeting human CAR T cells (Hu07BBz and Hu08BBz). Intracellular cytokine (IFNγ) staining was performed after these CAR T cells were co-cultured with human and canine IL-13Rα2 protein controlled with BSA. CD8 staining was used to distinguish CD4- and CD8-positive T cell groups on the x axis. (C) The expression of canine IL-13Rα1 and IL-13Rα2 mRNA on various canine tumor cell lines (Camac2, CLBL-1, GL-1, Cacal3, Cacal5, BW-KOSA, CS-KOSA, MC-KOSA, and SK-KOSA) was detected with RT-PCR, controlled with canine GAPDH. The percentage of cytokine- (IFNγ, IL-2, and TNF-α) positive T cells in CD4- and CD8-positive T cell subgroups was analyzed for mRNA-electroporated IL-13Rα2-targeting (Hu07BBz and Hu08BBz) human CAR T cells and un-transduced T cells after co-culture with canine tumor cell lines mentioned before. (D) Two million Hu08BBz-transduced human CAR-positive T cells were injected i.v. after 7 days of five million MC-KOSA subcutaneous implantation (n = 5 per group). Tumor size was calipered and compared with the same amount of un-transduced T cell control group. Statistically significant difference of tumor growth was determined by linear regression. ****p < 0.0001. Data are presented as means ± SEM.