Figure 1.
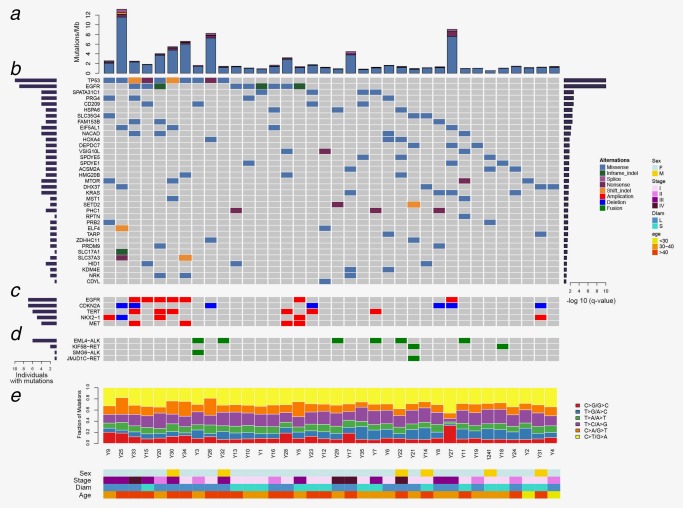
Mutation landscape of lung adenocarcinoma in young never‐smoker patients. (a) Nonsynonynous mutation rates (number of mutations per Mb) in 36 tumor samples. (b) Genes predicted to be significantly mutated by MuSiC. Asterisk indicated that the genes were noted by both MuSiC and MutSigCV. Genes were sorted by significant FDR value (right panel); the frequency was indicated by the number of mutated samples (left panel). (c) Focal CNVs in known lung cancer genes in 36 tumor samples. (d) SVs previously implicated in lung cancer in 36 tumor samples. (e) Percentage of six types of single nucleotide substitutions in each tumor sample. The samples were ordered on the horizontal axis based on the clustering of their mutated genes. The colors denoted different types of somatic events. [Color figure can be viewed at http://wileyonlinelibrary.com]
