Figure 1.
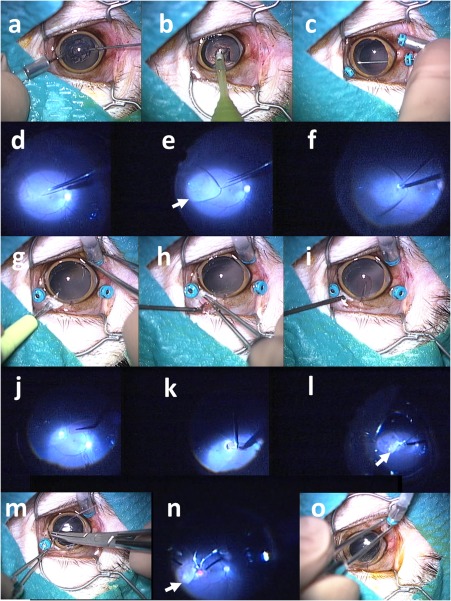
Surgical procedures (scenes) to implant retinal prosthesis OUReP in a monkey (No. 2–2). Total surgical time was 35 min. (a) Lens anterior capsule is cut with 25G vitreous cutter under irrigation with 25G infusion cannula in the anterior chamber. (b) Lens nucleus and cortex is aspirated with phacoemulsification tip from corneal incision. (c) Three 25G trocars are inserted over the conjunctiva through the sclera into the vitreous at 2 mm from the corneal limbus: an inferotemporal trocar is connected with infusion cannula, and the other two trocars are used for the vitreous cutter and light guide. Posterior capsule is cut with vitreous cutter. (d) After vitreous gel has been cut, subretinal fluid infusion is started with 38G tip. (e) Bleb retinal detachment (arrow) is made by irrigating solution infusion with 38G tip. (f) A retinal tear (retinotomy) is made by retinal coagulation with 25G bipolar diathermy. (g) Scleral incision is made with a knife after conjunctival incision. (h and i) A sheet (2.5 × 5 mm) of dye‐coupled film is inserted through scleral incision with 20G subretinal forceps. (j) Film is inserted into the vitreous with 20G subretinal forceps. (k) Film is inserted into subretinal space through a retinal tear with 20G subretinal forceps. (l) Fluid‐air exchange in the vitreous cavity is done with 25G vitreous cutter in aspiration mode to reattach the retina. (m) Scleral and conjunctival incisions are sutured. (n) Laser photocoagulation is applied around the retinal tear. (o) After gas tamponade with 30% sulfur hexafluoride, trocars are removed. Note subretinal dye‐coupled film (arrows in l and n).
