Figure 3.
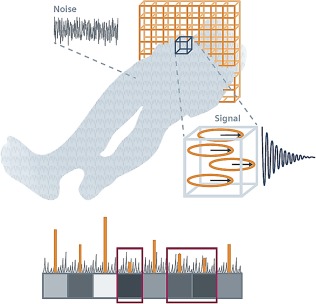
Noise in the image appears as a grainy random pattern similar to snow on a TV screen. It represents statistical fluctuations in signal intensity that do not contribute to image information, and have two basic sources: Brownian motion of molecules in the human body and electronic noise of the receiver, which both add up. If the signal from a slice is too weak, it may be “washed over” by noise (Courtesy of Ref. 93).
