Figure 11.
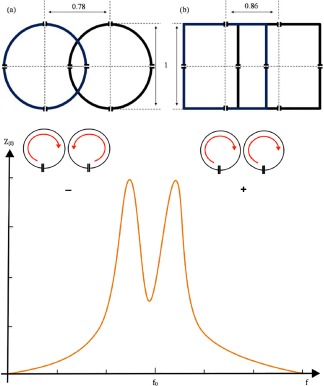
The behavior of two loops with resonance frequency f 1 = 1/[2π√(L 1 C 1)] and f 2 = 1/[2π√(L 2 C 2)] can be described with the impedance curve. The mutual inductance increases as the distance between the coils decrease, meaning that moving the loops further the two peaks will fuse to one. If the coupling between two coils gets stronger, they over‐couple and the resonance frequency splits into two current modes: a co‐rotating (+) and a counter‐rotating (–) mode. The optimal distance for geometrical decoupling depends on the loop dimensions. The ideal distances for maximal passive/inductive decoupling depend on the loop shape and size (a), (b).
