Figure 3.
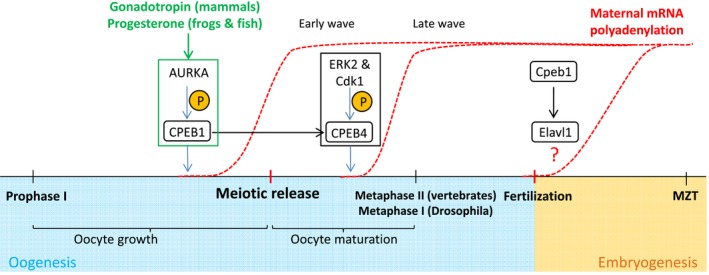
Different waves of maternal mRNA activation throughout oogenesis and early embryogenesis mediated by cytoplasmic polyadenylation. Maternal mRNAs are synthesized throughout the period of oocyte growth and stored in a dormant state. The first wave of activation is stimulated by GH or progesterone, resulting in phosphorylation of CPEB1 by Aurora kinase and the cytoplasmic polyadenylation of several maternal factors required for oocyte maturation. Another late wave is in turn mediated by CPEB4 whose translation was activated during the early wave and is phosphorylated by ERK2 and Cdk1 kinases. Following fertilization, another wave of cytoplasmic polyadenylation occurs on thousands of maternal transcripts. This later wave is required for the embryo to undergo a proper process of MZT. However, the exact molecular mechanism regulating this third wave of cytoplasmic polyadenylation has not yet been worked out.
