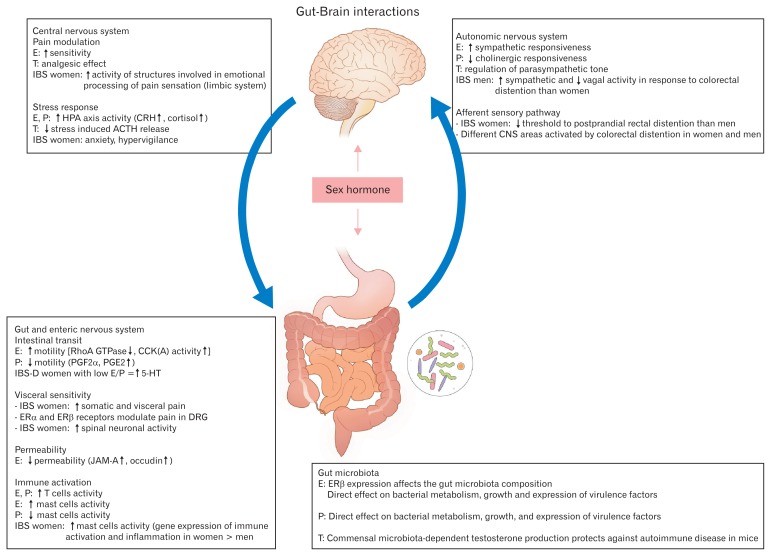
Figure 2.
Brain-gut axis and sex hormones interaction in irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Sex hormones influence peripheral and central regulatory mechanisms involved in the pathophysiology of IBS contributing to the alterations in stress response, visceral sensitivity and motility, intestinal barrier function, and immune activation of intestinal mucosa. Sex hormones also have direct effects on the gut microbiota and enteric nervous system. E, estradiol; T, testosterone; P, progesterone; CRH, corticotropin-releasing hormone; ACTH, adrenocorticotropic hormone; GTP, guanosine-5’-triphosphate; CCK, cholecystokinin; PG, prostaglandin; 5-HT, 5-hydroxytryptamine; ER, estrogen receptor; DRG, dorsal root ganglion; JAM, junctional adhesion molecule. Adapted from Meleine and Matricon.46