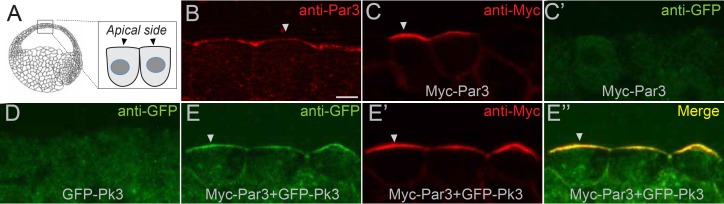
Figure 6. Par3 recruits Pk3 to the apical side of the cell in vivo.
Embryos were injected with GFP-Pk3 and Myc-Par3 RNAs (100 pg each), cryosectioned at stage 10.5 and immunostained with indicated antibodies (A) Scheme showing a relative position of imaged superficial ectoderm cells. Both endogenous Par3 (B), and exogenous Myc-Par3 (C, E’, E’’) are apically localized. (C’) Lack of Myc-Par3 staining with anti-GFP antibody. (D) Lack of apical enrichment of exogenous GFP-Pk3. (E–E’’) Myc-Par3 recruits GFP-Pk3 to the apical surface. (B, C, E) Apical enrichment is shown by arrowheads. The apical recruitment of Pk3 was observed in > 90% of cells coinjected with Pk3 and Par3. Each group contained five embryos. The same results were obtained in five independent experiments. Scale bar 10 µm.