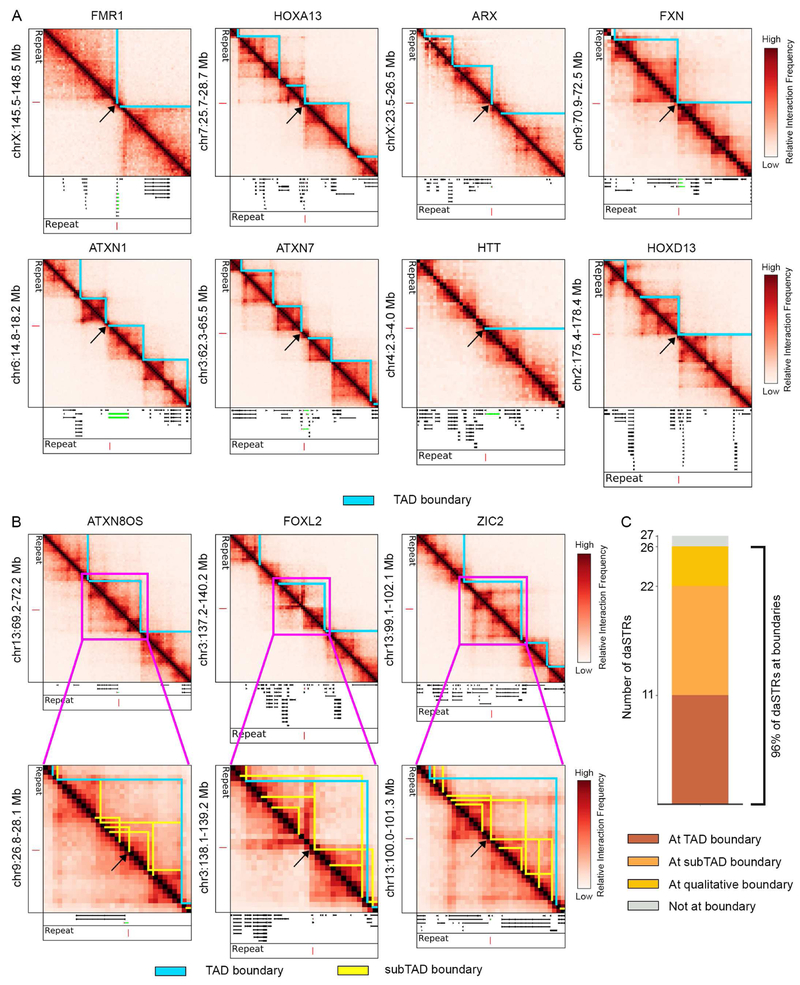
Figure 2. Disease-associated STRs (daSTRs) are significantly more likely to be found at domain boundaries compared to matched, normal-length repeats genome-wide.
(A) Empirical distribution of genomic distance from daSTRs and matched repeats to the nearest domain boundary. Of the 27 daSTRs analyzed in this study, CSTB was excluded from the statistical test because normal-length matched repeats were not found in the hg19 reference genome. (B) Bar plots comparing localization of daSTRs and matched repeats at boundaries or not at boundaries. (C) Bootstrapped distributions of percent daSTRs or matched repeats overlapping boundaries. (D) Percent daSTRs overlapping boundaries compared to a null distribution consisting of 10,000 draws of randomly sampled (n=26) matched, normal-length repeats.