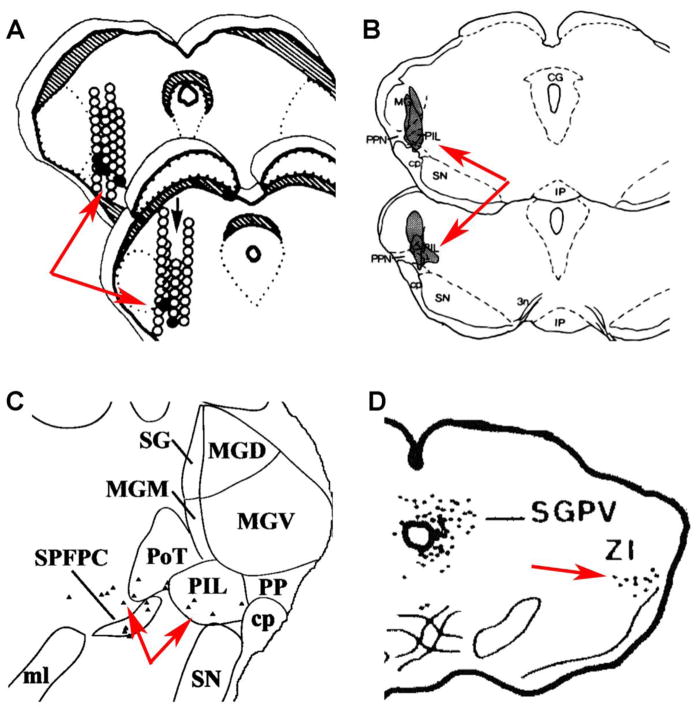
Fig. 6.
Presumed diencephalic relay center of the milk-ejection reflex. The panels are modifications from the reference papers. The red arrows point to the presumed relay station of suckling information. A: Black circles represent the position where microstimulations evoked, and empty circles where could not evoke milk ejection (Tindal and Knaggs, 1975). B: Lesion of the shaded areas with NMDA injections reduced milk ejection (Factor et al., 1993). C: Black triangles correspond to neurons retrogradely labeled following injection of tracer into the PVN (Campeau and Watson, 2000). D: Black dots represent neurons retrogradely labeled following injection of tracer into the supraoptic nucleus (Tribollet et al., 1985). Abbreviations: CG–central gray (or substantia grisea, or periaqueductal gray), cp–cerebral peduncle, IP–interpeduncular nucleus, MG–medial geniculate body, MGD, medial geniculate body, dorsal subdivision, MGM - medial geniculate body, medial subdivision, MGV - medial geniculate body, ventral subdivision, ml–medial lemniscus, PP (or PPN)–peripeduncular nucleus, PIL–posterior intralaminar thalamic nucleus, PoT, Posterior thalamic nucleus, triangular subdivision, SG–suprageniculate nucleus, SGPV–substantia grisea periventricularis, SN–substantia nigra, SPFPC–subparafascicular nucleus, parvocellular subdivision, ZI–zona incerta, 3n–oculomotor nerve.