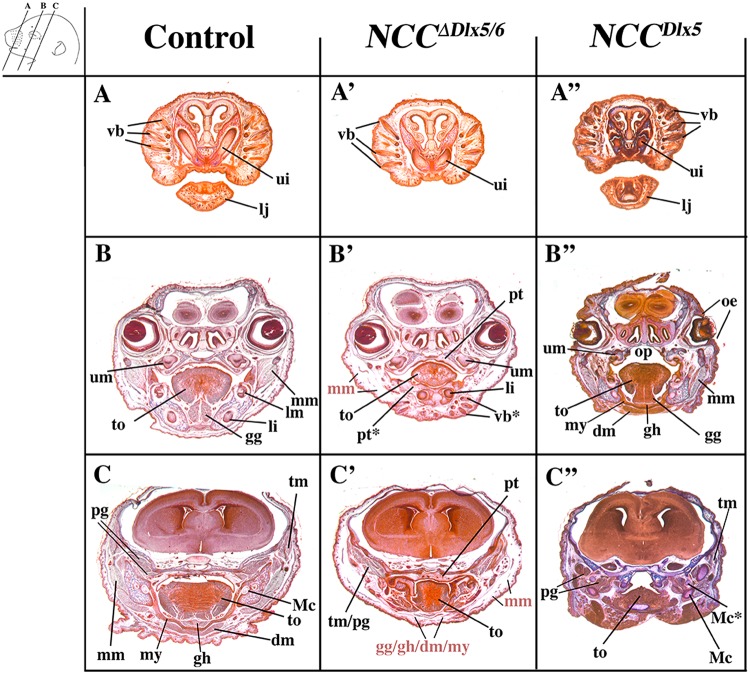
Figure 5.
Representative cranial frontal sections of E18.5 control, NCC∆Dlx5/6 and NCCDlx5 mouse foetuses. The planes of section are indicated in the upper left insert. Compared to control foetuses (A–C), NCC∆Dlx5/6 foetuses (A’–B’) present ectopic vibrissae (vb*) in the lower jaw (B’), reduced and disorganized tongue musculature (to), absence of masseter, digastric, mylohyoid, geniohyoid and genioglossus muscles while the temporal and pterygoid muscles (tm, pg) form but show defective attachments on the transformed lower jaws. The midline fusion of the transformed dentary bone of NCC∆Dlx5/6 foetuses gives rise to a palate-like structure in the lower jaw (pt*) with folds reminiscent of palatine rugae. NCCDlx5 foetuses (A”–C”) present open eyelids (oe), an open palate (op), ectopic Meckelian-like cartilages, relatively normal tongue and associated musculature and mispatterned masticatory muscles adapted to the transformed skeletal elements. Abbreviations: dm, digastric muscle; gg, genioglossus muscle; gh, geniohyoid muscle; li, lower incisor; lm, lower molar; lj, lower jaw; Mc, Mekelian cartilage; Mc*, duplicated Mekelian cartilage; mm, masseter muscle; mx maxillary bones; mx*, transformed dentary bone; my, mylohyoid muscle; oe, open eyelids; op, open palate; pg, lateral and medial pterygoid muscles; pt palate; pt*, ectopic palate-like structure resulting from midline fusion of lower jaws; px, premaxillary bone; ui, upper incisor; um, upper molar; tm, temporal muscle; to, tongue; vb, vibrissae; vb*, ectopic vibrissae. Abbreviations in light red represent muscles that did not differentiate and are replaced by loose mesenchymal tissue.