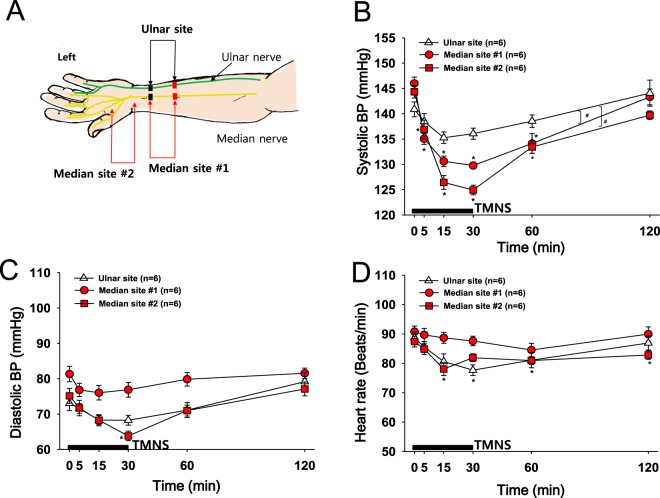
Figure 4.
Effects of electrical stimulation of the skin over the median or ulnar nerve on hypertension. (A) Experimental scheme. Location of electrodes for stimulation of the median nerve (Median site #1 and #2) or ulnar nerve (Ulnar site) sites and measurement of BP and HR. (B–D) Changes in systolic BP (B), diastolic BP (C) and HR (D) following electrical stimulation (10 Hz) of the skin innervating the median or ulnar nerve on the left hand. Decreases in systolic BP were more profound following the stimulation of the median nerve sites (Median site #1 & #2) than the stimulation of the ulnar nerve site (Ulnar site; A). Electrical stimulation of the palm side of the thumb (Median site #2) also tended to decrease diastolic BP and HR. *p < 0.05 vs. the value obtained before TMNS (Time 0). #p < 0.05 vs. the Ulnar site.