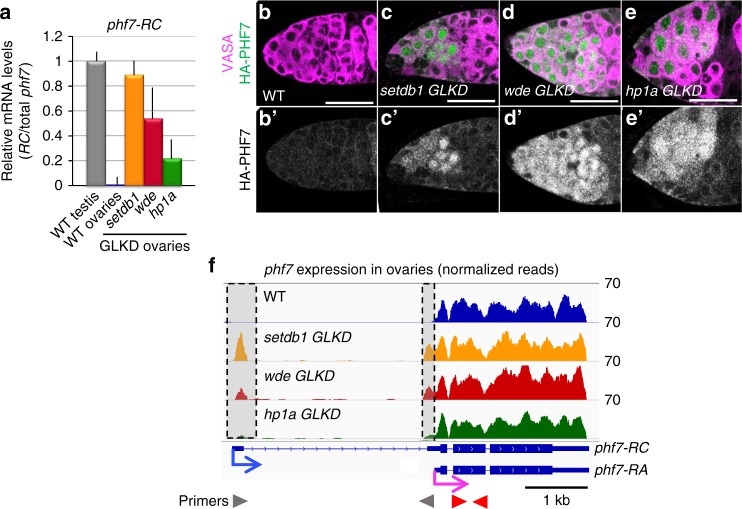
Fig. 2.
SETDB1, WDE, and HP1a depletion leads to female-to-male reprogramming at phf7. a Depletion of H3K9me3 pathway members leads to ectopic expression of the testis-specific phf7-RC isoform. RT-qPCR analysis of the testis phf7-RC transcript in wild-type testis, wild-type and mutant ovaries. Expression, normalized to the total level of phf7, is shown as fold change relative to testis. Primers are shown in panel F. Error bars indicate standard deviation (s.d.) of three biological replicates. b–e Depletion of H3K9me3 pathway members leads to ectopic expression of the testis-specific PHF7 protein. Ovaries from animals carrying an HA-PHF7 transgene stained for HA (green, white in B’-E’). Germ cells were identified by α-VASA staining (magenta). Scale bar, 25 μm. f RNA-seq data confirms ectopic expression of the testis-specific phf7-RC isoform. Genome browser view of the phf7 locus. Tracks show RNA-seq reads aligned to the Drosophila genome (UCSC dm6). All tracks are viewed at the same scale. The screen shot is reversed so that the 5’ end of the gene is on the left. The reads that are unique to the mutant ovaries are highlighted in gray. The two phf7 transcripts, phf7-RA and phf7-RC, are indicated. phf7-RC is normally only expressed in testis (blue arrow). phf7-RA is normally expressed in ovaries (pink arrow). Primers for RT-qPCR are indicated by arrowheads: gray for phf7-RC, red for total phf7