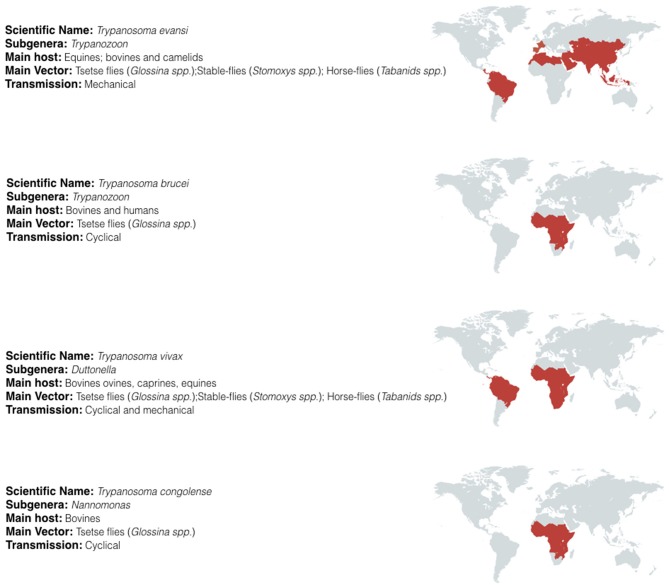
Figure 1.
Geographic distribution of salivarian trypanosomosis. Salivarian trypanosomosis is a worldwide problem caused in large by Trypanosoma evansi, Trypanosoma brucei (including the human infective subspecies T. b. gambiense and T. b. rhodesiense), Trypanosoma vivax and Trypanosoma congolense. T. brucei, and T. congolense infections are limited to the sub-Saharan tsetse belt. In contrast, as T. vivax and T. evansi can be mechanically transmitted, these parasites have migrate beyond the tsetse belt, out of Africa and into South America and Asia [adapted from (18–22)].