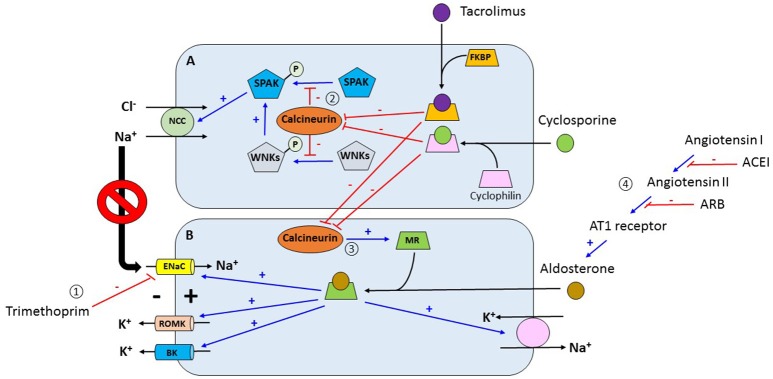
Figure 1.
(1) Trimethoprim inhibits the activity of ENaC in the late distal convoluted convoluted tubule and cortical collecting duct which decreases the electrical gradient for channels. (2) Tacrolimus and cyclosporine bind to FKBP and cyclophilin respectively forming complexes. These complexes inhibit calcineurin which is a phosphatase. Under normal conditions, calcineurin retrieve phosphate groups from different proteins including SPAK and WNKs. Inhibition of calcineurin allows for the phosphorylation of these kinases which activate NCC increasing sodium chloride reabsorption in the distal convoluted tubule. Increasing sodium reabsorption in this nephron segment decreases the delivery of sodium to more distal segments which in turn decreases the electrical gradient for potassium secretion via ROMK channels. (3) Activation of MR by aldosterone increases the activity of proteins associated with potassium excretion in the distal nephron including ENaC, ROMK, BK, and the Na+-K+-ATPase pump. In addition, calcineurin increases the expression of the mineralocorticoid receptor. In contrast, tacrolimus and cyclosporine, by inhibiting calcineurin, decrease the decrease the expression of the mineralocorticoid receptor with subsequent reduction in potassium Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers inhibit aldosterone with the subsequent reduction in potassium excretion. ENaC, epithelial sodium channel; ROMK, renal outer medullary potassium channel; FKBP, FK binding protein; SPAK, STE20/SPS1-related proline- and alanine-rich kinase; WNKs, with no-lysine kinases; NCC, sodium chloride cotransporter; MR, mineralocorticoid receptor; BK, big potassium channel. (A) Distal convoluted tubular cell. (B) Principal cell of collecting duct.