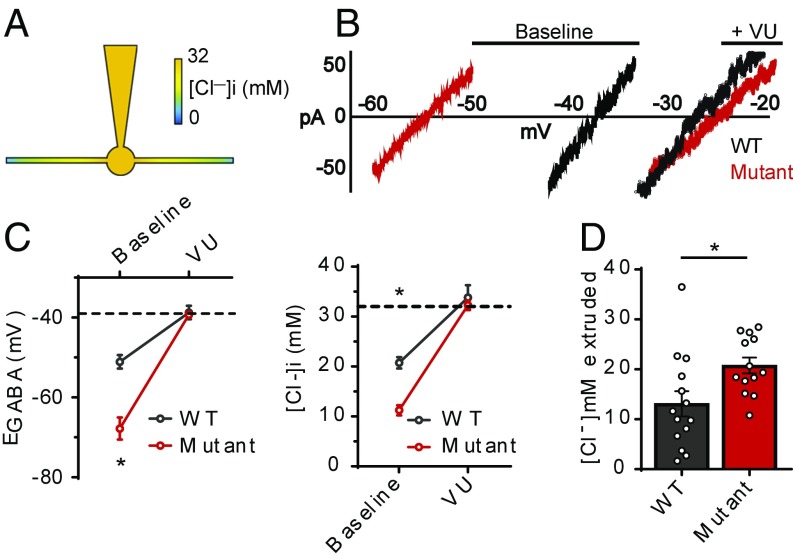
Fig. 6.
KCC2-T906A/T1007A mutations enhance the rate of KCC2-mediated Cl− extrusion. (A) Cartoon of whole-cell patch-clamp Cl− loading assay that creates a somatic−dendritic Cl− gradient. (B) I–V plot of leak-subtracted muscimol currents depicting the EGABA values, both before and after exposure to the KCC2 inhibitor VU0463271 (VU) (I–V plots depict results before correction for liquid junction potentials; see Materials and Methods). (C) EGABA values were more negative in KCC2-T906A/T1007A neurons compared with WT, indicating that the rate of Cl− extrusion is increased by the KCC2-T906A/T1007A mutations. The EGABA values were shifted to the expected value of approximately −39 mV (dashed line) when VU was applied. The corresponding [Cl−]i values are also shown, with the 32-mM [Cl−]i indicated by the dashed line. *P < 0.0001. (D) The concentration of Cl− that was extruded under baseline conditions was greater in the KCC2-T906A/T1007A neurons, calculated as the difference between [Cl−]i under baseline and VU conditions. *P < 0.05.