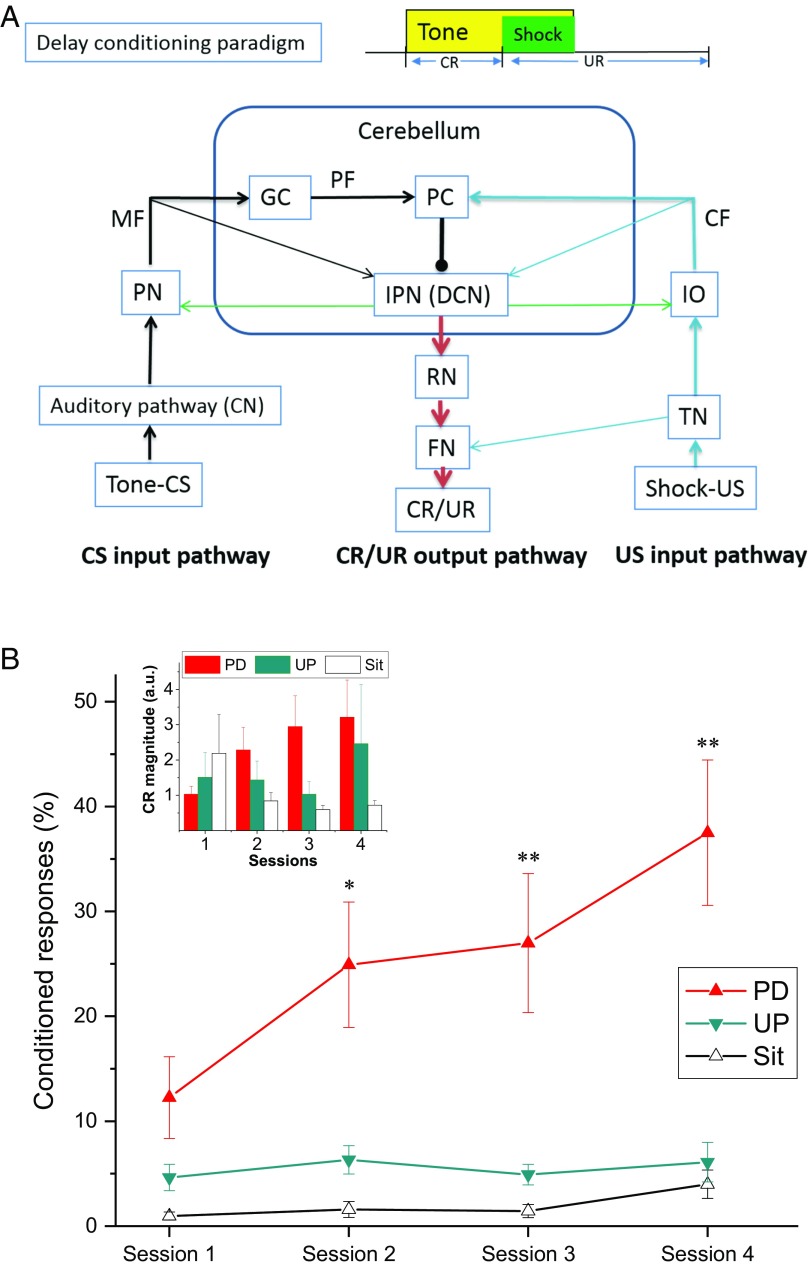
Fig. 1.
The mean percent (±SEM) of CRs during delay eyeblink conditioning. (A) The delay conditioning paradigm and the underlying neuronal circuitry. (B) The mean percent CRs (CRs%) for rats in the Paired (PD), Unpaired (UP), and Sit groups. The Inset in B shows that the CR magnitude for the Paired group increased with training sessions compared with Unpaired and Sit groups. Note that the Paired group showed greater CRs% than the Unpaired and Sit groups across the four sessions of delay eyeblink conditioning, which suggests the acquisition of learning. Asterisks denote values for the Paired group that are significantly different from those for the Unpaired and Sit groups (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01). CF, climbing fiber; CN, cochlear nucleus; FN, facial nucleus; GC, granule cell; IO, inferior olive; IPN, interpositus nucleus; MF, mossy fiber; PC, Purkinje cell; PF, parallel fiber; PN, pontine nuclei; RN, red nucleus; TN, trigeminal nucleus; UR, unconditioned response.