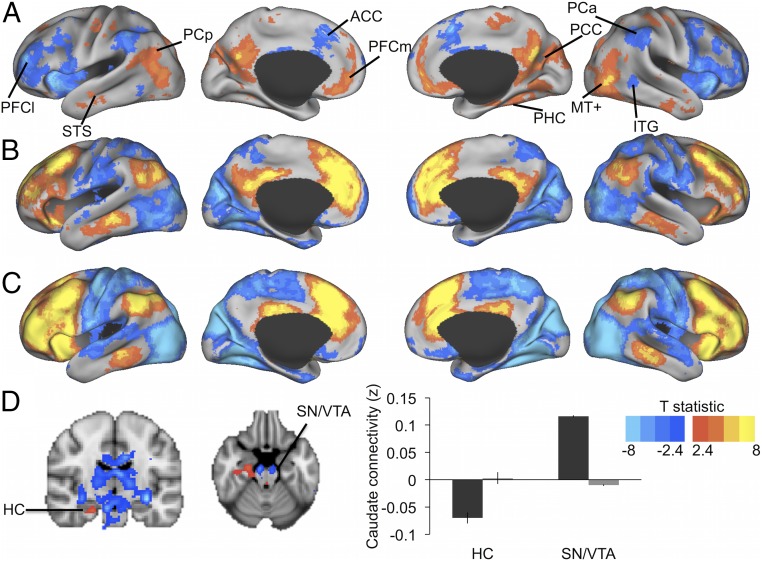
Fig. 3.
Whole-brain fc of a bilateral caudate FPN seed [Montreal Neurological Institute (MNI): x = −12, y = 10, z = 8; x = 12, y = 10, z = 8]. (A) Older > young adults = red-yellow; older < young adults = blue. ACC, anterior cingulate cortex; ITG, inferior temporal gyrus; MT+, middle temporal area; PCa, anterior inferior parietal cortex; PCC, posterior cingulate cortex; PCp, posterior inferior parietal cortex; PFCl, lateral prefrontal cortex; PFCm, medial prefrontal cortex; PHC, parahippocampal sulcus; STS, superior temporal sulcus. (B and C) Mean connectivity map for older (B) and younger (C) adults. Red-yellow regions are positively connected with the seed, blue regions negatively. (D) Age group differences in subcortical connectivity with the caudate FPN seed. Older > young adults = red-yellow; older < young adults = blue. For illustration, mean functional connectivity estimates are shown thresholded at T > 2.4 (P < 0.01). Bar graph illustrates mean connectivity of the caudate FPN seed with the hippocampus (HC) and midbrain (SN/VTA) by age group (older adults = gray bars; younger adults = black bars).