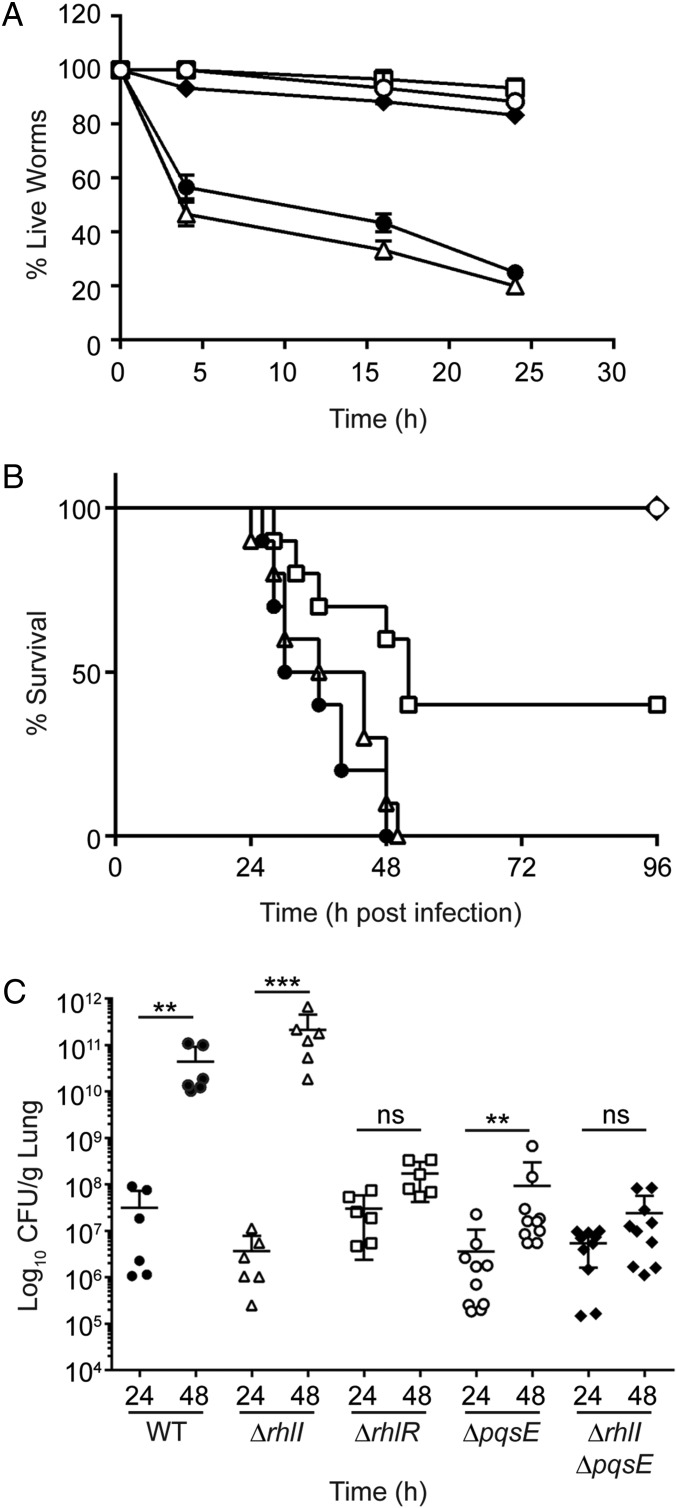
Fig. 3.
PqsE is required for RhlR-dependent virulence in animal infection models. (A) C. elegans were applied to lawns of WT PA14 (closed circles), the ΔrhlR mutant (open squares), the ΔrhlI mutant (open triangles), the ΔpqsE mutant (open circles), and the ΔrhlI ΔpqsE double mutant (closed diamonds). Error bars represent SEM of three independent replicates. (B) For survival experiments, BALB/c mice were infected intratracheally with ∼3 × 106 cfu of WT PA14 or the indicated mutants and were monitored for up to 4 d postinfection. Symbols as in A. Results are represented on Kaplan Meier curves and were compiled from two independent experiments; n = 10. Significant differences were calculated by log rank test by comparing each strain to the WT (ΔrhlI; P = 0.374, ΔrhlR; P < 0.01, ΔpqsE; P < 0.0001, ΔrhlI ΔpqsE; P < 0.0001). (C) Bacterial burden recovered from mice at 24 h and 48 h postinfection with WT PA14 or the indicated mutants. Results were analyzed by one-way ANOVA. Multiple comparisons were performed between the indicated points for each strain. ***P < 0.001; **P < 0.05; ns, not significant.