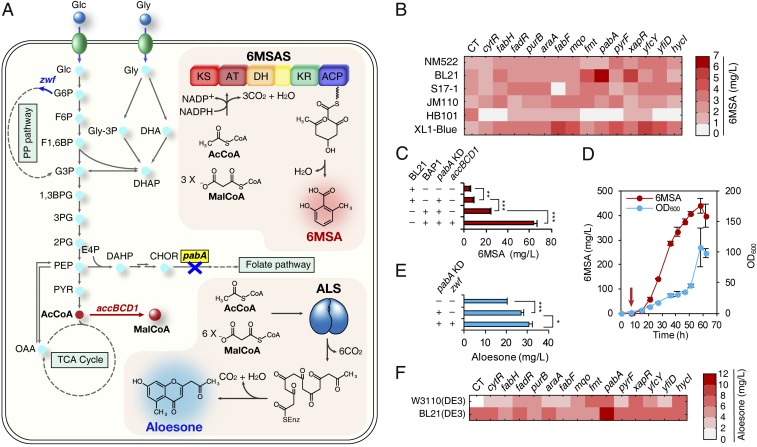
Fig. 4.
Application of the screened knockdown gene targets for the increased production of polyketides. (A) The biosynthetic pathways of 6MSA and aloesone. Blue X (along with gene written in bold letters surrounded by yellow box) indicates that the corresponding gene was knocked down. Red bold arrow indicates that the corresponding gene was overexpressed for 6MSA production; blue bold arrow indicates that the corresponding gene was overexpressed for aloesone production. Gray dotted lines indicate omitted pathways. The upper box describes the heterologous 6MSA biosynthetic pathway. The lower box describes the heterologous aloesone biosynthetic pathway. Each gene or gene cluster encodes the following: accBCD1, acetyl-CoA carboxylase from C. glutamicum; pabA, para-aminobenzoate synthetase; zwf, glucose 6-phosphate 1-dehydrogenase. (B) Results of combinatorial 6MSA production in test tubes. The 6 E. coli strains selected among the initial 16 strains for their higher 6MSA production (SI Appendix, Fig. S9D) were introduced with each of the 14 synthetic sRNAs for enhanced malonyl-CoA accumulation and thus increased 6MSA production. The gene names written horizontally represent the 14 knockdown gene targets. CT, control (without sRNA). The displayed average values were calculated from two biological replicates. (C) Enhanced production of 6MSA by flask cultivation. The +/− signs for BL21/BAP1 indicate host strain selection. The +/− signs for pabA KD/accBCD1 mean whether pabA knockdown or accBCD1 overexpression was implemented in the production host. Error bars, mean ± SD (n = 3). **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, determined by two-tailed Student’s t test. (D) Fed-batch fermentation of the best 6MSA producer (E. coli BAP1 harboring pTac-Pg6MSAS, pWAS−anti-pabA and pBBR1-accBCD1). The red arrow denotes isopropyl β-d-1-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) induction time point. The red line denotes 6MSA production and the blue line denotes cell growth represented as OD600. The displayed average values were calculated from two biological replicates. Error bars, mean ± SD (n = 2). (E) Enhanced production of aloesone by flask cultivation. The +/− signs for pabA KD/zwf mean whether pabA knockdown or zwf overexpression was implemented in the production host. Error bars, mean ± SD (n = 3). *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001, determined by two-tailed Student’s t test. (F) Results of combinatorial aloesone production in test tubes. Two E. coli DE3 strains were introduced with 14 synthetic sRNAs for enhanced malonyl-CoA accumulation and thus increased aloesone production. The gene names written horizontally represent the knockdown gene targets. CT, control (without sRNA). The displayed average values were calculated from two biological replicates. Abbreviations: 1,3BPG, 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate; 2PG, 2-phosphoglycerate; 3PG, 3-phosphoglycerate; 6MSAS, 6MSA synthase; AcCoA, acetyl-CoA; ACP, acyl carrier protein; ALS, aloesone synthase; AT, acyltransferase; CHOR, chorismate; DAHP, 3-deoxy-d-arabinoheptulosonate 7-phosphate; DH, dehydratase; DHA, dihydroxyacetone; DHAP, dihydroxyacetone phosphate; E4P, d-erythrose 4-phosphate; F1,6BP, fructose 1,6-bisphosphate; F6P, fructose 6-phosphate; G3P, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate; G6P, glucose 6-phosphate; Glc, glucose; Gly, glycerol; Gly-3P, glycerol 3-phosphate; KR, ketoreductase; KS, ketosynthase; MalCoA, malonyl-CoA; OAA, oxaloacetate; PEP, phosphoenolpyruvate; PYR, pyruvate.