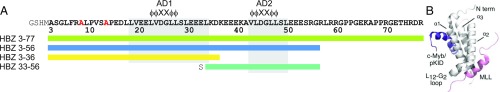
Fig. 1.
(A) HBZ AD constructs used in the experiments. The KIX-binding regions of the AD1 and AD2 domains are highlighted with gray boxes and the conserved amphipathic ΦΦXXΦΦ (Φ is a bulky hydrophobic residue; X represent any hydrophilic amino acid) binding motifs within each domain are indicated. Two N-terminal alanine residues in red were mutated from cysteines. Additional N-terminal residues in gray are from recombinant protein production. (B) Structure of the KIX:cMyb:MLL ternary complex (6), showing the binding sites on KIX (gray) occupied by the activation domains of c-Myb (purple) and MLL (pink).