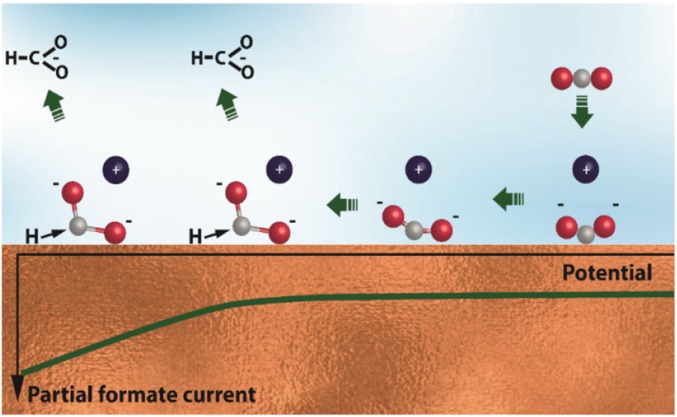
Fig. 7.
Proposed model of CO2 activation on a Cu electrode in aqueous electrolyte. η2(C,O)-CO2− is formed at potentials anodic of the electrocatalytic current. Cathodic polarization gradually activates this species (elongates the C–O bonds and decreases the O–C–O angle), which is accompanied by weakening of its Cu–C bond and stabilization of the Cu–O bond. The electrocatalytic reaction starts when η2(C,O)-CO2− is able to participate in the second electron transfer, for example, to react with *H to produce formate. Atom colors: red, oxygen; gray, carbon.